Background
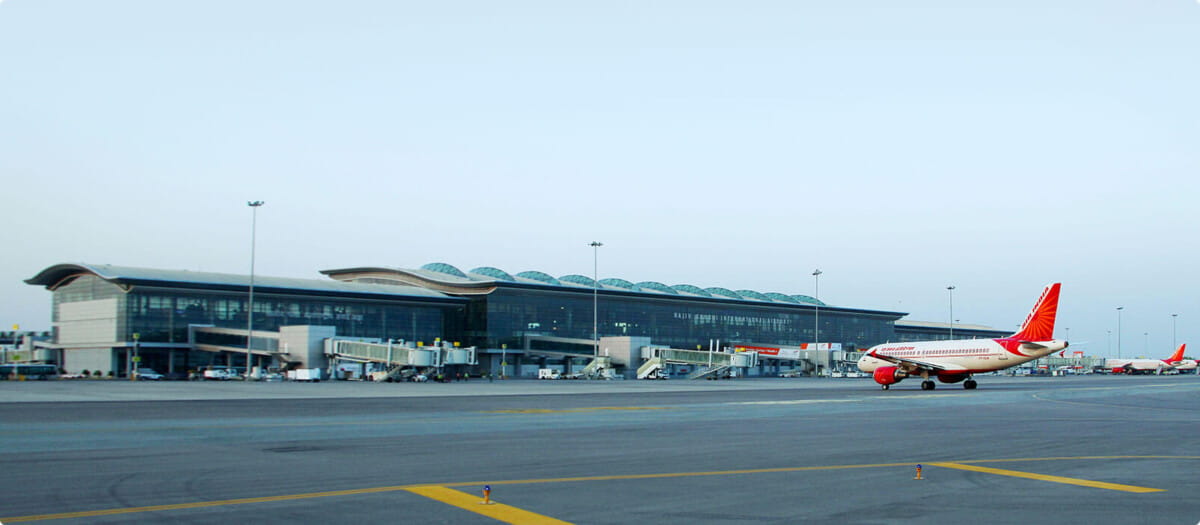
Rajiv Gandhi International Airport (RGIA), located in Hyderabad, is India’s first greenfield airport developed under the Public-Private Partnership (PPP) model. Spanning 5,500 acres, it is one of the largest airports in the country. RGIA plays a vital role in handling over 21 million passengers annually and was the first airport in India to introduce both domestic and international e-boarding services, setting new standards for efficiency and innovation in air travel.

Challenge
A key design challenge at RGIA was ensuring that the automatic smoke vents and make-up air vents met the required opening angles. Considering the large size and weight of the operable panels, achieving proper functionality and safety compliance was a complex task. Moreover, laying the extensive cables needed to connect window actuators and controllers across the vast airport infrastructure posed significant logistical hurdles. The integration of this system into the overall fire safety framework required careful planning to ensure that the smoke extraction system would operate reliably during emergencies.
Solution
To meet these challenges, bespoke chain actuators were developed and installed, tailored to the specific weight and dimensions of the smoke and make-up air vents. The system was also equipped with multi-point locking (MPL) actuators that work in conjunction with the chain actuators to meet weather performance standards. When the system is activated, the MPL actuators disengage the locking pins, allowing the chain actuators to open the vents. Upon resetting the fire alarm panel, the system operates in reverse, with the chain actuators closing the vents and the MPL actuators re-engaging the locking pins.
The smoke vents, which are bottom-hung and open outward, were designed to release smoke and heat from the building during the early stages of a fire. This early smoke extraction helps control its spread, enhances visibility, and provides safer evacuation routes. The top-hung make-up air vents, which also open outward, allow fresh air to enter the building, improving the natural extraction of smoke through roof hatches and ensuring balanced airflow for more effective smoke removal.
The system was integrated with a robust controller network, ensuring reliable and seamless operation during fire emergencies. All components adhere to international safety standards, such as EN12101, ensuring that RGIA’s safety systems meet global benchmarks. Additionally, the system is fully integrated with the Building Management System (BMS), enabling the maintenance and operations team to monitor the health and status of the controllers in real-time. This proactive communication allows for early detection of potential issues, improving operational efficiency and ensuring the reliability of the system.
The implementation of this advanced system not only enhanced the overall safety of the airport but also demonstrated the innovative use of technology in large infrastructure projects, setting a new standard for both safety & operational efficiency.
Quick Facts:
- Project: Rajiv Gandhi International Airport
- Location: Hyderabad, Telangana
- Client: Alufit International Pvt Ltd
- Architect: Aedas, Hong Kong
- Consultant: EDRC, L&T Construction Buildings & Factories
- Concept Facade Consultant: Meinhardt Façade Technology