Fire and life safety are the prime motto while designing the building. All the stakeholders, viz-a-viz the architect, consultants, client, PMC, and anyone involved in the project design and execution, should understand and take this on priority.
There are two ways to protect the building from fire: Active fire protection and passive fire protection. There is a code requirement of a 2-hour fire-safe building envelope for high-rise buildings. Most of the buildings are being constructed using the RCC, AAC blocks and fly ash bricks, which themselves give good fire protection. Glass is an integral part of architectural design, but fire-safe glass has a major cost impact. That too can be balanced out by using active protection techniques.
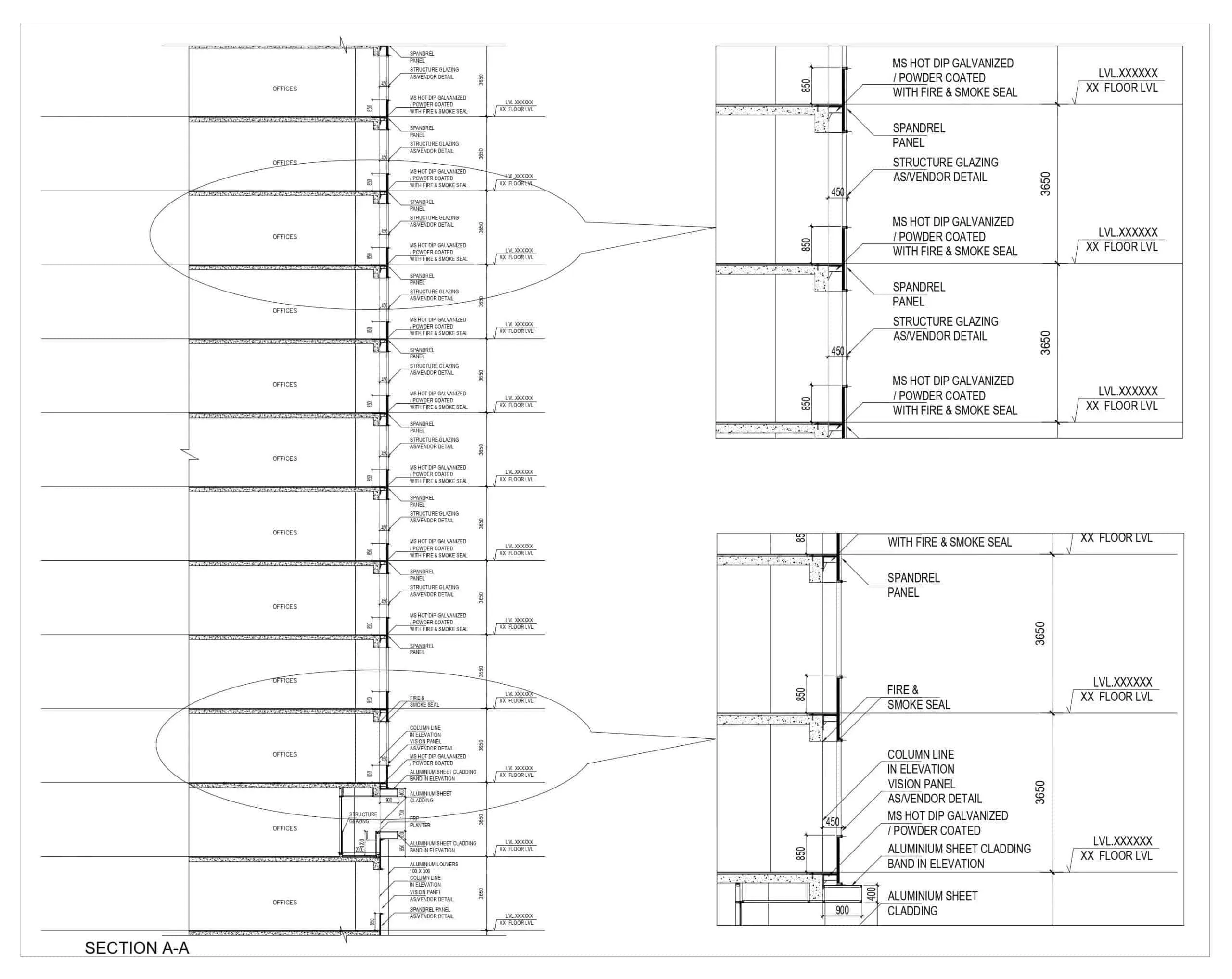
The fire protection system varies from case to case, considering the utility type and height of the building. Active fire protection systems are heat and smoke detectors, fire hose reels, ventilation fans, sprinklers, gas-based suppression systems, fire extinguishers, emergency lighting, and public address systems. Passive fire protection systems are fire doors, fire compartmentation, smoke seals, intumescent compound, fire curtains and fire dampers.
There are number of tests listed in the National Building Code of India, and also listed in International Codes NFPA 285 (standard fire test method for evaluation of fire propagation characteristics of the exterior – Non-load-bearing wall), ASTM E2307 (standard test method for determining the fire resistance of perimeter fire barrier systems using intermediate-scale, multi-story test apparatus), ASTM E84(surface burning characteristics of building material), BS8414, EN 13501-1 (fire classification of construction products and building elements. Classification using data from reaction to fire tests), BS EN 13823 (Single burning item) and ISO 13785 for the fenestration systems.
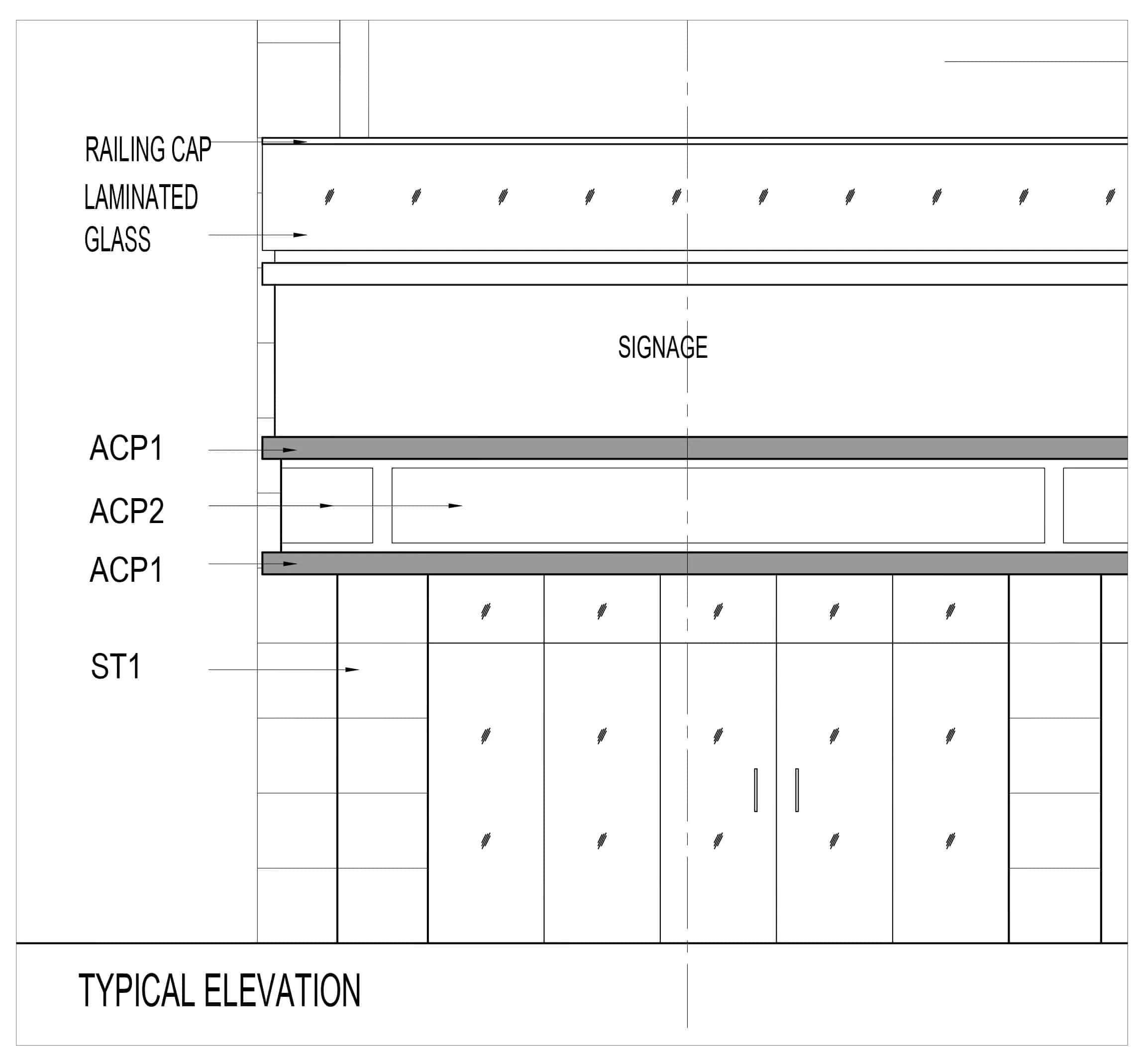
The drawings and detailing for the wall assembly are very important, and the selection of the material also plays a vital role in facade design with respect to fire and life safety. We cannot test every material installed on the façade, but we should consider the complete wall assembly (cross-section of the element) while testing for fire. The majority of the materials used in the fenestration should be compliant with life and safety codes. There are certified testing labs available, where we can ask for the fire testing certificate from the suppliers, and if in doubt, it can be randomly retested.