Breaking The Coordination Bottleneck: How Systemic Delays Are Undermining India’s Façade Engineering Excellence
India’s entire construction landscape is undergoing an unprecedented transformation. Mirrored within the glowing towers of Gurgaon to smart cities across the subcontinent, façade systems have transcended their boundaries as building envelopes in the modern age, coalescing into a complex, performance-critical assembly defining thermal comfort, energy efficiency, fire safety credentials, and long-term propositions defining a building’s attractiveness or value.
However, lurking ominously under this architectural renaissance is a latent issue that could undermine industry performance: delays in coordinating key stakeholders that are essential for successful project execution. The delays between architects, façade consultants, MEP engineers, structural designers, and project managers are more than mere inconveniences regarding schedule. They can be seen as institutional barriers through which technical excellence is compromised, costs are inflated, and innovation is stifled throughout the industry.
Recent industry analysis reports that over 70 per cent of major façade projects face delays due to coordination issues in tier-one cities in India. They suffer, on average, scheduling overruns of about 12–16 weeks as a direct consequence of stakeholder misalignment. Dislodged from the lifecycle of the project, however, these delays cause irrevocable loss of technical integrity in the building envelopes that, in fact, determine occupant comfort and energy performance across decades.
The Sequential Design Trap
It is at this juncture that the project delivery methodology adopted by the Indian construction industry in façade integration falls short when compared with international project delivery methodologies. Most Indian projects follow a sequential, compartmentalised design process, conceived as an add-on to the building rather than an integral component of it.
Consider a typical workflow: architects finalise schematic and design development drawings in isolation. Structural and MEP systems are subsequently designed around these parameters—before, and oftentimes at tender or GFC stage, the façade consultant enters the project. Cascading technical compromises throughout the entire project lifecycle create a situation of life-and-death importance to the whole project.
In fact, this leads to severe consequences: structural embed provisions do not deliver façade load requirements, and this necessity involves tedious retrofits, adding costs of anywhere between 15 and 20 per cent of structural budgets. Based solely on aesthetics, window-to-wall ratios are fixed in such a way that there are buildings requiring about 40 per cent additional cooling energy compared with optimally designed alternatives. MEP interfaces also become inaccessible afterthoughts, compromising practicality and maintenance protocols.
However, India’s diverse climate zones present their greatest challenges. Conditions ranging from humid coastal areas to arid inland regions represent very different types of façades in terms of performance requirements. The freezing of architectural concepts before façade consultants are hired puts an end to possibilities for responsive design optimisation and project success.
Perhaps of greater concern is the industry-wide practice of foregoing early-stage envelope strategy development. Typically, developers progress through feasibility phases without any establishment of key façade performance parameters – target U-values, Solar Heat Gain Coefficients, air infiltration rates, fire resistance requirements, and maintenance strategies. Industry studies report that early-stage envelope strategies save 25-30 per cent in façade costs, with approvals taking 40 per cent longer to obtain through building-permit systems.
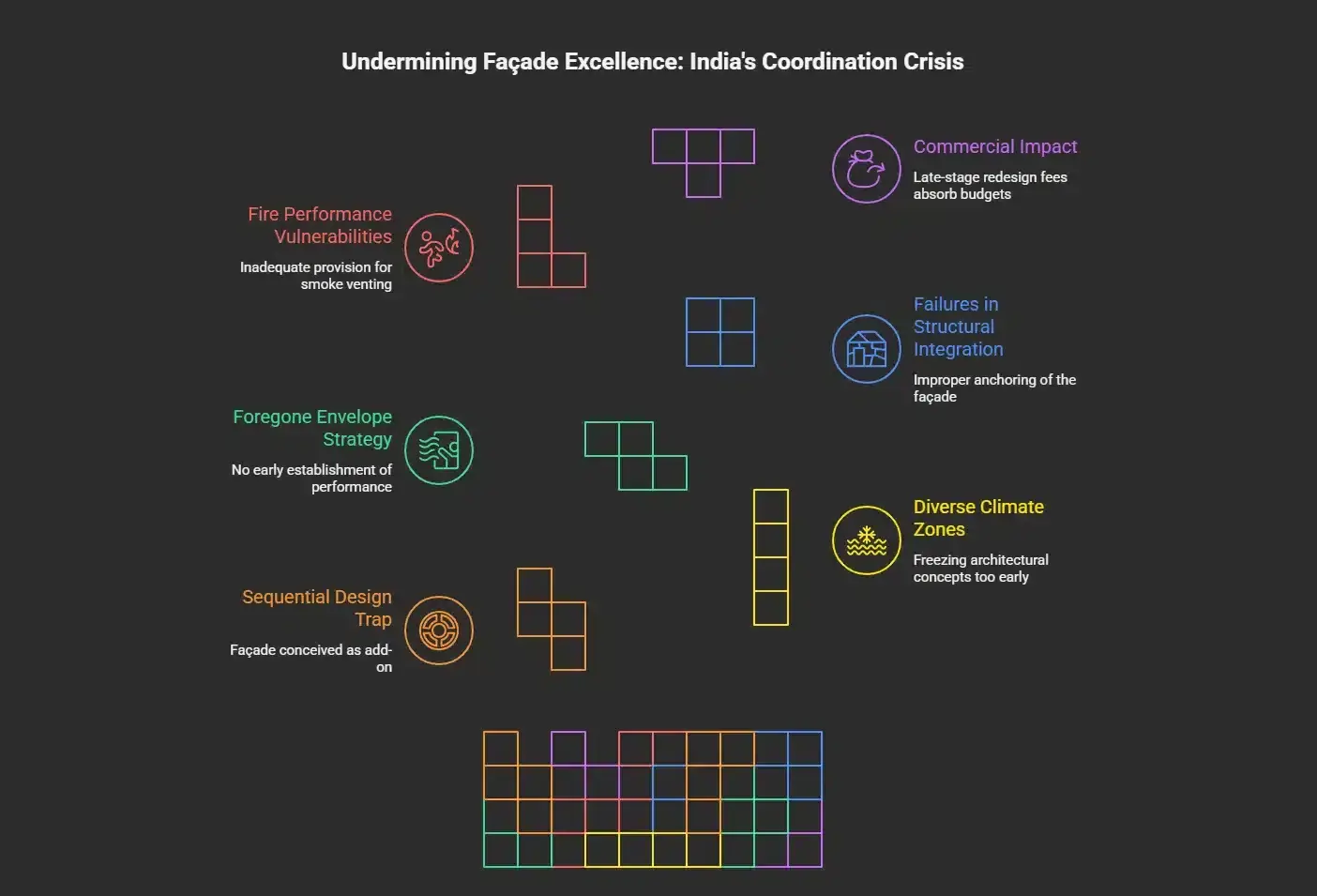
Technical Consequences: Where Coordination Gaps Become Performance Failures
The technical implications of poor coordination go far beyond scheduling delays to basic performance compromises that would eventually affect the operation of the building for decades into the future.
Failures In Structural Integration
The most critical of its failure modes is improper anchoring of the façade. When structural teams design away from façade load data, the result is misaligned cast-in channels or inadequate bracket provisions, which further compromise slab edge coordination. These cause very expensive structural retrofits — often core drilling and epoxy anchoring – that could cost three times more than what would have been spent on properly planned cast-in systems.
It is not about the cost. It compromises joint integrity regarding seismic action, raises questions of proper tolerance in movement accommodation, and creates potential for poor wind load resistance – all of which fundamentally affect the safety of the building, all the more critical in seismically active areas of India.
Fire And Energy Performance Vulnerabilities
Fire safety compliance has specific vulnerabilities caused by coordination breaches, increasing concerns that have arisen following recent NBC updates regarding fire safety in India. The lack of an efficient fire stop or inadequate provision for smoke venting in façades crossing compartmentation lines could delay occupancy approvals for 6–12 months and could lead to retrofitting costs between 15 and 20 per cent of original budgets.
On the thermal performance and energy fronts, the stakes are equally high, particularly in light of the ambitious Energy Conservation Building Code targets set by India. Improperly specified glares or poorly detailed visual barriers with no coordinated shading systems may increase HVAC loading by up to 30 per cent. Such deterioration in performance, even worse, has been experienced in India’s extreme climates, where a building could consume up to 40–50 per cent more energy than optimally designed alternatives due to façade miscoordination.
Commercial Impact: The Hidden Cost Of Coordination Failure
Commercial implications continue to stretch far beyond direct cost overruns. Late-stage redesign fees for façade alterations tend to absorb 3–5 per cent of façade budgets, which is significant when façades cost about 15–20 per cent of total construction costs in buildings. Emergency procurement requirements for custom profiles inflate material costs by 20–30 per cent and extend delivery schedules by 8–12 weeks.
Schedule impacts tend to be equally expensive, especially during monsoon-affected construction periods in India. Façades generally require lead times of about 10–16 weeks, in addition to a few buffer weeks owing to monsoon logistics. Delays in releasing “For Construction” drawings create cascading delays in shop drawing development and mock-up construction before final fabrication.
Ultimately, the delays affect weather seal completion, thus impacting the scheduled times for interior works, HVAC commissioning, and occupancy permits. In Mumbai’s commercial market, every month of delayed occupancy could cost property developers about 2–4 per cent of total rental income potential, hence making coordination efficiency a very important competitive advantage.
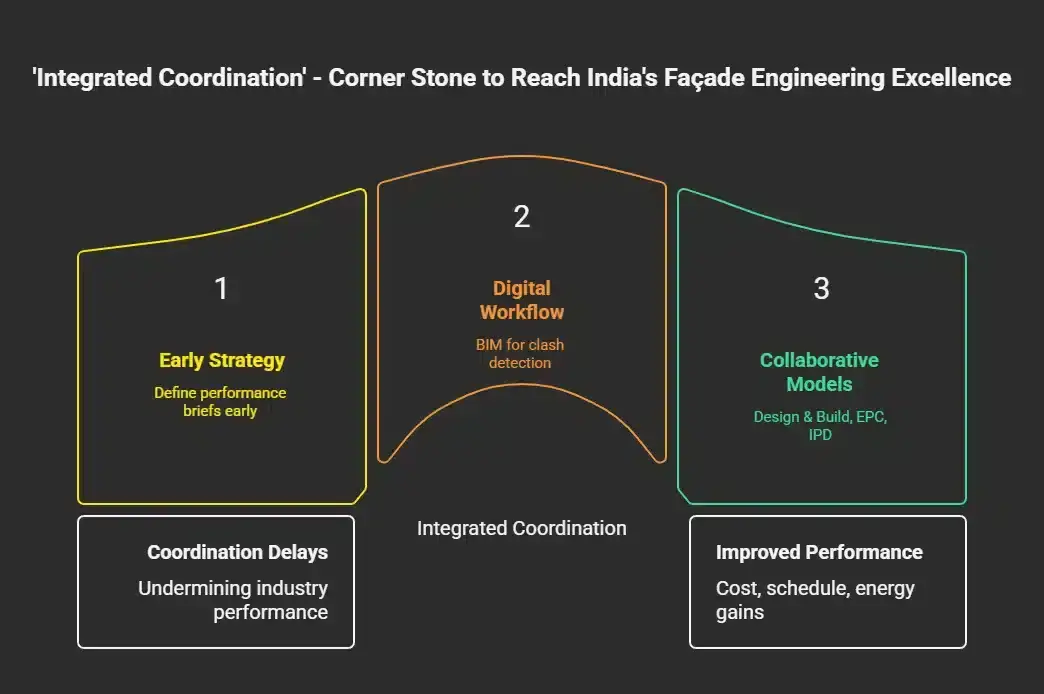
Strategic Solutions: Reframing Façade Integration
Changes are required in the approach to project delivery, stakeholder engagement methods, and technology adoption strategies to truly address delays in coordination.
Early Façade Strategy Integration
This means, among other aspects, the clear definition of envelope performance briefs early in the conceptual stage in terms of environmental performance metrics, budget parameters, fire safety requisites, and maintenance protocols.
Façade consultants should also be engaged during Stage 1 and Stage 2 design discussions so that the requirements of the façade inform rather than react to architectural and structural decisions. The leading developers in India are displaying the benefits of this approach. Some projects in Gurgaon achieved a 15-20 per cent reduction in façade costs and improved schedules by almost 30 per cent through façade consultants being brought on board during the schematic design stage.
Early in the project, leading property developers in Mumbai achieved a 25–30 per cent reduction in energy consumption from early façade–HVAC coordination protocols.
Digital Workflow Integration
Integration of a digital workflow means that technology adoption does not stop at BIM but goes further to require Level of Detail 350+ modelling across all trades. All elements at the interface of a façade — such as anchors, louvres, and fire collars – must also be included in digital clash detection protocols.
A new building completed in Pune claimed to have installed 95 per cent of its façade free of clashes through systematic BIM coordination protocols, which cut down installation time by 25 per cent and eliminated costly field modifications. Introducing collaborative procurement and delivery models reflects a shift in project delivery methodology from traditional design-bid-build to Design & Build, EPC, or even Integrated Project Delivery. These collaborative approaches enable early vendor feedback on system feasibility and cost implications.
Consider, for instance, some notable developers based in Chennai who established early contractor engagement through integrated design–build delivery methods, resulting in 20 per cent reduced façade costs and 35 per cent improved schedules.
The Path Forward: Industry Transformation
Cultural transformation is the necessity on the road ahead, as it positions façade integration at the very heart of design development. This demands better collaboration protocols, systematic technology adoption, and performance-based decision-making.
Conclusion
Projects that embrace integrated façade coordination achieve 15–25 per cent cost reductions, 30–40 per cent schedule improvements, and 25–35 per cent enhancements over traditionally coordinated projects in energy performance. Without improvements at the fundamental level, India certainly cannot achieve those lofty sustainability targets under the National Solar Mission and Energy Conservation Building Code. The technical sophistication of today’s façade systems demands coordination that matches the excellence their performance potential can achieve.
Coordination delays in façade engineering form the basic blocks to achieving technical excellence, commercial success, and environmentally friendly performance in this rapidly transforming industry in India. For project teams, developers, and industry stakeholders, façade coordination is not a luxury — it is a fundamental requirement for project success in an increasingly performance-driven market.
The question is not whether or not industry stakeholders will move toward integrated coordination practices. It is a matter of propelling the systematic changes necessary — and doing so swiftly – to unlock the full potential of façades. The future belongs to those who embrace proactive, integrated methodologies to deliver façades.














