Expert Insights Into Challenges And Solutions
Façade projects play a critical role in both the aesthetic appeal and functional integrity of buildings, but they come with a range of challenges and risks. From material selection and structural integrity to environmental factors and safety compliance, façade systems must be meticulously designed and maintained to ensure long-term durability and occupant safety. Advanced technologies like AI-driven predictive tools, BIM, and simulation models are transforming risk management practices, making façade design and maintenance more effective and reliable.
In this article, industry experts provide insights into the complex challenges, especially in material choice, structural calculations, and adherence to safety standards, associated with façade projects, highlighting key risks and indicators of issues.

Identifying Risks In Façade Projects
Façade projects face numerous risks due to complex interactions between materials, structure, and environmental factors. Dasun Siriwardena, DGM – Design & Engineering at Aparna-Craft Exteriors Pvt Ltd., notes that improper integration of materials and inadequate thermal or acoustic performance may lead to issues that only become apparent post-installation. Structural failures, often resulting from incorrect wind load calculations, can pose severe safety threats. Other issues like inadequate fire resistance and poor drainage can lead to water infiltration, while poor material choices may result in thermal expansion or visible deformation.
To mitigate these risks, advanced AI-driven Building Information Modelling (BIM) tools offer predictive insights by identifying potential weak points in the façade design before construction begins. Additionally, early-stage machine learning models help evaluate material performance, allowing design teams to suggest optimised alternatives. Siriwardena points out common signs of façade problems, such as visible deformation, condensation, and discolouration from material degradation. These issues can be detected early using drone-based inspections, combined with AI image analysis for real-time diagnostics, reducing the risk of costly repairs or replacements in the future.
Key Risk Areas In Façade Projects
According to Mohit Sehgal, Head of Façade (North) at Rysn Infra LLP, façade projects face risks across several areas:
- On-site delays can often occur due to various reasons, such as bad weather or the availability of materials.
- Health and safety are vital at all stages of a project, but especially onsite when the risk of an incident is often the greatest.
- Communication during the design process is key to avoiding wastage.
- Risks post-installation are also present, such as corrosion.
- Replacement parts can prove difficult to find if the company no longer supplies them.
- If Building regulations are not met, companies risk prosecution.
The Role Of Expert Oversight
Vishal Chawhan, Architect and Town Planner, emphasises the importance of engaging experienced façade consultants and contractors, noting that façade projects with specialised elements are at high risk if expert oversight is lacking. According to Chawhan, having a façade consultant on board ensures the façade aligns with the architect’s vision and meets the intended specifications. An experienced contractor further reinforces this by executing the façade with precision, adhering to both design and safety standards.
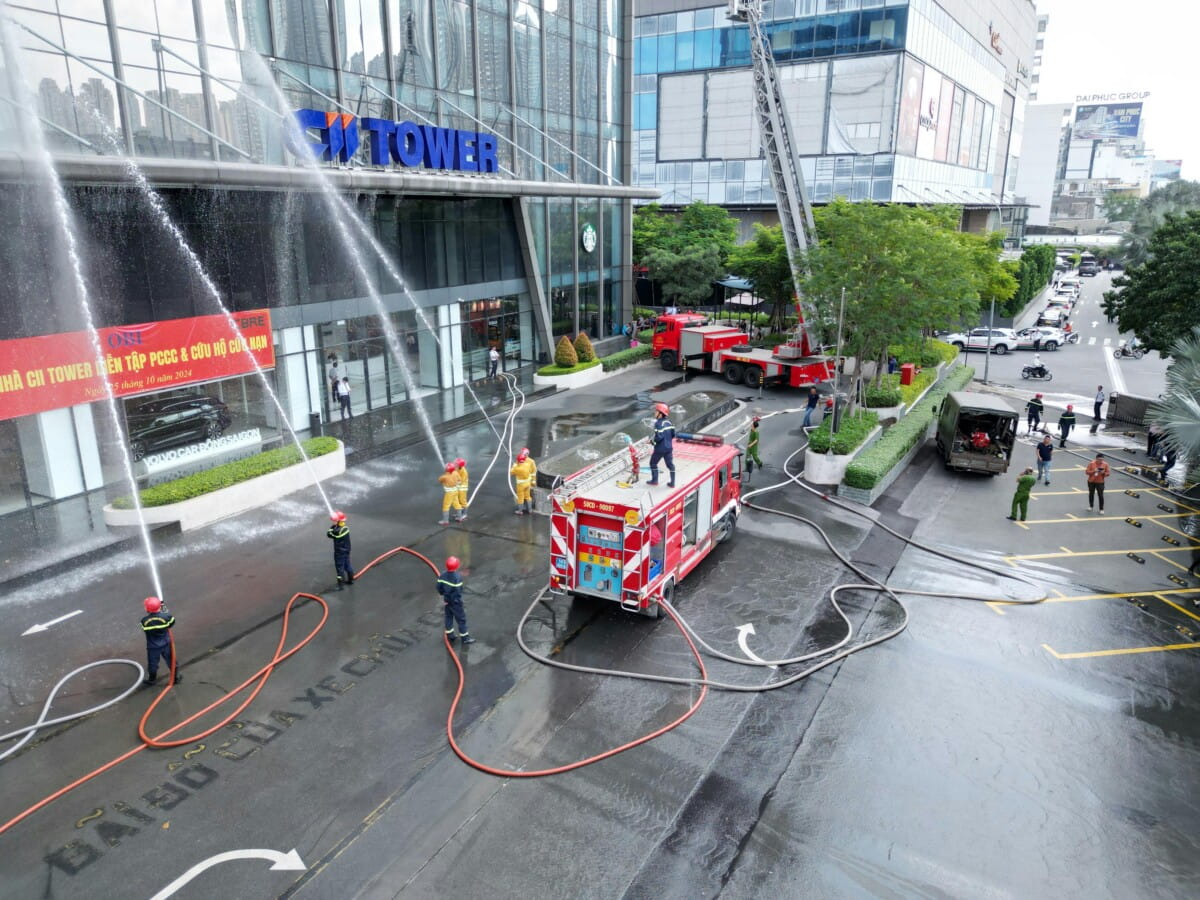

Indicators Of Façade Issues At Different Stages
Façade-related issues typically emerge during two key stages:
- The Pre-Construction Stage includes design, detailing, and selecting an execution agency. At this stage, architects, structural consultants, and façade consultants must work in close collaboration to achieve a flawless design. However, challenges often arise when selecting the execution agency. In the Indian market, for instance, the emphasis on competitive pricing sometimes leads to performance compromises. The specifications are diluted, and critical elements such as fire stops and moisture barriers are sometimes sacrificed to cut costs. A team approach is necessary to ensure performance standards are maintained without bowing to price pressures.
- Post-Construction Stage: Any compromises made during the pre-construction phase become apparent at this stage. Structural failures, leaks, and visible cracks in the façade are primary indicators of underlying problems. By this point, the original team, including architects, structural consultants, and façade specialists, is usually no longer involved, leaving occupants to address these issues. Repairs often result in further erosion of quality, as pricing considerations dominate the repair process, and the involvement of expert teams is rare.
Criteria For Selecting Façade Materials
Choosing materials for façades involves considerations for fire resistance, structural stability, and durability. Siriwardena highlights the role of advanced simulations and AI-driven analytics in predicting material behaviour under environmental stresses, helping teams select optimal materials.
Compliance with fire safety standards, such as EN 13501 and NFPA 285, is also essential.
Sehgal advocates for materials tested for fire resistance, with fire safety considerations extending beyond façades to include evacuation, detection, and suppression systems for a comprehensive safety approach.
Chawhan emphasises context-specific material selection based on factors like climate, occupancy, and seismic risks, requiring close collaboration between architects, structural engineers, façade consultants, and contractors to create a balanced and appropriate selection of materials tailored to the project’s unique demands. While there is no universally perfect choice, this teamwork approach enables the selection of materials that meet safety, performance, and aesthetic goals for each façade project.
Ensuring Safety In High-Rise Façades
For high-rise buildings, façade systems must withstand wind pressures, heavy rains, and seismic forces. Siriwardena notes that computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations, supported by AI, help predict wind pressure distribution in urban settings. Virtual wind tunnel tests, incorporating real-time weather data, refine these models to ensure structural stability. For water and air penetration, parametric tests simulate rainfall and wind-driven water ingress to evaluate system resilience. Seismic stability is assessed through dynamic structural analysis software, which uses AI to simulate the performance of flexible joints and façade systems under varying earthquake scenarios based on regional seismic activity.
Sehgal stresses that façades in high-rise structures must prioritise wind load considerations to avoid structural failures. Sehgal adds that façade engineering must prioritise wind load considerations, as high winds impose significant stress on a building’s exterior, potentially leading to damage or structural failure if inadequately designed.
Chawhan outlines a three-stage testing process for façade safety: virtual simulations, on-site mock-up testing, and post-installation evaluations. This rigorous approach ensures compliance with safety standards and long-term durability.
Secure Anchor Design In Façade Systems
Designing anchor systems for façades involves precision to manage environmental loads. Siriwardena explains that finite element analysis (FEA) helps visualise stress distribution across anchor points, while AI-driven predictive maintenance software tracks anchor performance over time. During load testing, robotic arms simulate conditions like wind gusts and thermal expansion, enabling proactive maintenance and strengthening system resilience.
Load testing applies various force levels to test anchor reliability under different conditions. AI-enhanced robotic systems facilitate precise testing, while fatigue testing under extreme conditions forecasts the lifespan of façade anchors.
Real-time sensor data is used post-installation for monitoring, with AI-driven predictive maintenance software that flags potential issues based on performance changes over time. During load testing, AI-driven robotic arms simulate environmental stresses like wind gusts, thermal expansion, and seismic activity. Fatigue testing under extreme conditions, supported by AI algorithms, predicts long-term wear and enables proactive maintenance.

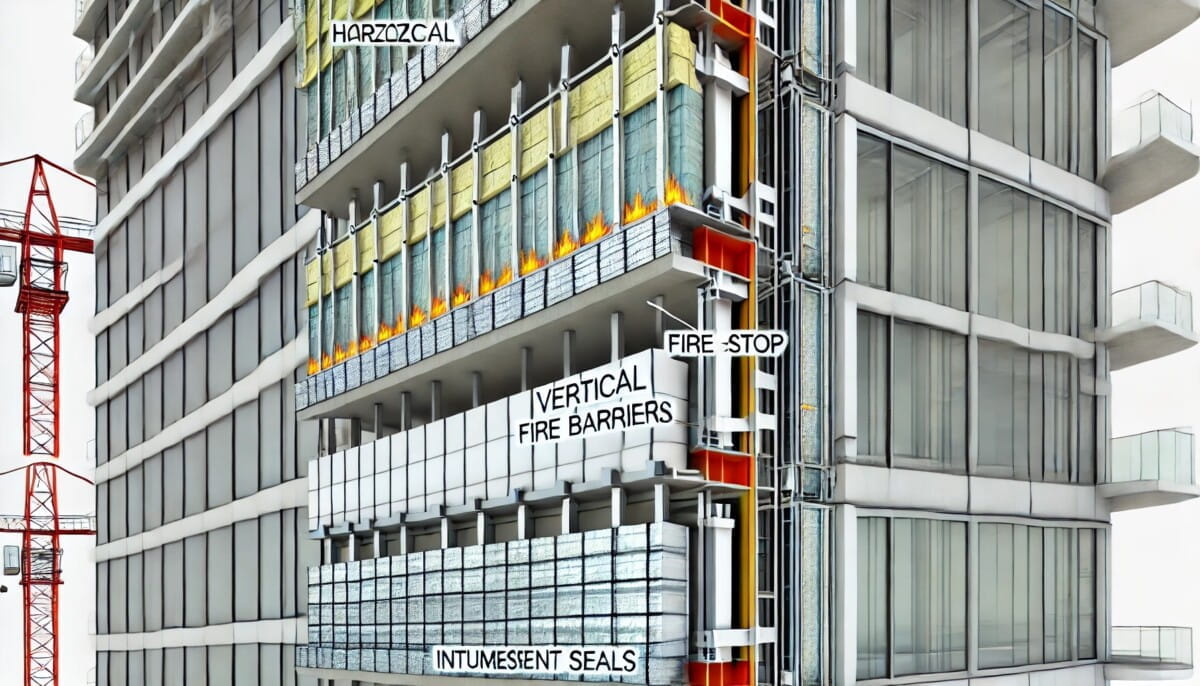
Fire-Stop Systems And Compartmentalisation For Safety
Fire-stop systems are crucial for containing fire and smoke within buildings. Siriwardena shares that AI-driven fire simulation models are used to predict fire spread in different façade configurations, allowing for optimal fire-stop placement. Horizontal and vertical compartmentalisation, using fire-resistant materials like intumescent coatings, prevents fire from spreading across floors. Real-time sensors embedded in façades can detect early signs of fire, allowing for immediate response.
Sehgal explains that effective compartmentalisation minimises the “chimney effect,” where air pressure can push fire and smoke through a building. Building codes, such as India’s National Building Code (NBC) and Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), mandate compartmentalisation to control fire spread. Following these standards, fire-stopping materials are strategically placed on separate floors, enhancing safety.
Enhanced Fire Safety Through Compartmentalisation
Fire-stop systems & compartmentalization are essential for fire safety in high-rise façades. Siriwardena notes that using fire-resistant materials and intumescent coatings within façades helps contain fire spread between floors. Real-time sensors in the façade detect signs of fire, allowing for prompt intervention and fire-stopping adjustments.
Maintenance Access And Safety In High-Rise Façades
For high-rise façades, safe access for cleaning, maintenance, and repairs is essential. Dasun Siriwardena highlights the use of Building Maintenance Units (BMUs) equipped with AI features, which optimise cleaning schedules based on environmental conditions and wear patterns. IoT sensors embedded in façades monitor wear, reducing the need for manual inspections. Drones with AI-powered vision systems inspect façades, identifying areas needing maintenance without requiring workers to access dangerous spots.

Maintenance Protocols For Façade Safety
Mohit Sehgal emphasises that façade maintenance requires a detailed manual outlining cleaning protocols and safety procedures, tailored to each building’s unique requirements.
Key Safety Practices Include:
- Safety Harnesses and Anchors: Workers use safety harnesses connected to secure lines, regularly inspected for integrity.
- Ascenders and Descenders: These devices allow safe vertical navigation and are used with safety lines.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Essential PPE, such as helmets and gloves, shields workers from hazards like falling debris.
- Weather Considerations: Maintenance activities are scheduled based on weather conditions to maximise safety.
- Training: Proper training in equipment handling and safety protocols reduces risks.
- Routine Equipment Inspections: Regular checks ensure that safety lines and harnesses remain in good condition.
- Emergency Response Plans: Every operation includes an emergency plan, ensuring quick responses to potential incidents.
- Risk Assessments: Thorough risk evaluations are conducted before any maintenance work.
Customised Access Solutions
Architects and façade consultants work together to design access systems suited to each building’s specific requirements. Chawhan emphasises that while standard systems are available, custom solutions may be necessary to balance aesthetics, functionality, and maintenance needs. This collaborative approach ensures the façade is both attractive and accessible for routine upkeep.

Moving Towards Safer Façade Design
Chawhan advocates for incorporating life-saving systems tailored for high-rise façades, especially in areas prone to extreme weather or seismic activity. He suggests collaboration between regulatory bodies, designers, and technology providers to enhance façade safety standards, ensuring resilience against environmental and structural risks. Through technology, rigorous protocols, and teamwork, façade safety in high-rise buildings can be assured, minimising risks and enhancing occupant safety.
Conclusion
Ensuring the safety, performance, and resilience of façade systems in modern buildings requires a collaborative approach that integrates expertise, technology, and stringent safety standards. By identifying risks early and employing advanced simulation and monitoring tools, façade professionals can address potential issues proactively, minimising costly repairs and ensuring occupant safety. Engaging experienced façade consultants and employing technology-driven solutions like AI-enhanced diagnostics and predictive maintenance software strengthens façade integrity. As high-rise buildings continue to rise in cities worldwide, investing in robust design and maintenance protocols will be essential for sustainable, safe, and visually compelling urban landscapes.