What Is Meant By A Sustainable And Efficient Fenestration?
In the current times, sustainability is the given way forward in the evolution of built environments. Various professionals have adopted different ways to meet this paradigm shift in the built environment by evolving design concepts, elements and materials that work together to achieve sustainability.
Though there are various guiding principles, contextual parameters play a very important role in determining the philosophies to be adopted to create a sustainable building. Sensitive selection of site with requisite feasibility analysis, appropriate orientation, and selection of building form and material are determinants. Building envelope and façade play an important role in achieving sustainability. The façade is the interface between the built space and it’s surrounding, and fenestrations are the mode of interaction between them. They hold a strategic position in the environmental performance of buildings. A sustainable fenestration would be a system that would streamline this interaction between the inside and outside without compromising on daylighting, ventilation, and views.
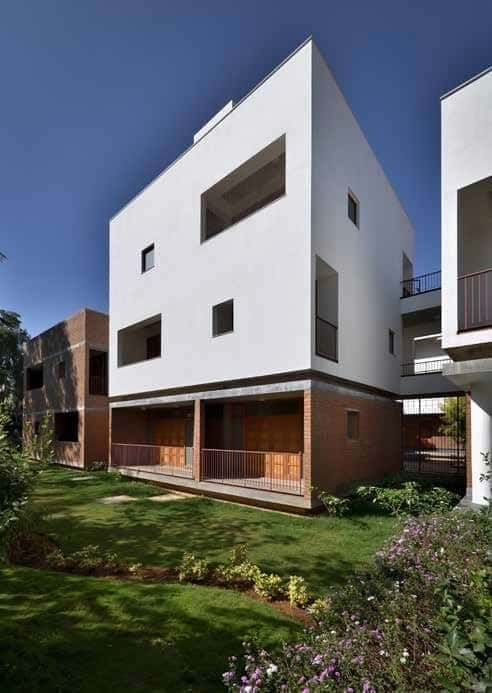

Talking About The Door Window Evaluation, What Should Be The Ideal Wall-To-Window Ratio?
The area of the door-window and its orientation are largely determined by the contextual parameters like the climatic zone in consideration, orientation of the window, outdoor air temperature, season, time, and occupancy pattern, etc. For example, in a hot, humid climate, openings are placed to ensure maximum cross ventilation, whereas in a dry, hot climate, the characteristics of the openings are to be controlled to minimise heat gain inside the building. Other factors like daylight requirements, views & vistas and occupancy pattern in the buildings further streamline the decision. The natural lighting performance is better when the window-wall ratio increases. However, windows also play a critical role in terms of building thermal insulation.
Hence, the ideal wall-window ratio is guided by the environmental factors and the occupancy pattern. Most of the codes prescribe a wall-to-window ratio of approximately 6:4 to help in achieving desirable indoor qualities and balancing the energy requirement. However, façades can be designed using a higher percentage than the code prescriptive maximum by using interior and exterior shading strategies combined with high-performance fenestration systems, which help to reduce the unwanted solar gain while still allowing for natural daylight to enter spaces.
How Can We Improve Acoustics Through Proper Design & Installation Of Doors & Windows?
Interior strategies and exterior design can be adopted improve the acoustics of a building. Starting sound from barriers recessing the building as far from the source of noise, use of plantations or solid boundary walls, sensitive location, and design of openings, installing soundproof fenestration systems, and use of appropriate acoustical solutions within the building can together improve the interior acoustical quality and experience of the building.
Natural sound barriers like plants and shrubs can fragment sound waves. A small lawn or a footpath right outside, and planting a line of tall shrubs can have an impact in cutting out the noise reaching the building.
Locating the openings in the façade away from the source of noise is the most obvious technique, and even the building form can be modulated in ways that can block exterior noise from entering the building without compromising daylight. Soundproof fenestration systems available in the market have exceptional sound absorption properties and can reduce street noise by up to 90%. Double-glazed acoustic windows absorb noise and ensure that it does not reverberate inside a room. Apart from blocking noise, soundproof glass also increases thermal comfort, is easy to install and maintain, provides UV protection, and reduces the amount of dust entering inside your home or office.
How Can We Improve Thermal Comfort Through Effective Fenestration?
The location, size, orientation, treatment and internal shading of the openings in the building have a significant impact on energy efficiency and comfort. In the Indian scenario, the southern sun is hot, so wherever possible, openings are minimised on the southern façade, or if provided, they are well shaded. Shading fenestrations on the southern façades without compromising the daylight can be tricky at times. Service spaces like toilets, stores, etc., are placed on the southern façade to add to the buffer to the primary occupied spaces. The northern daylight can be harnessed well for light, without much heat. The fenestrations on the east and west can be shaded using vertical barriers that can cut down the direct solar radiation while letting light in.
Using fenestration systems that are calibrated to provide thermal insulation on the building envelope also has a big role in reducing the solar heat gain. Well-designed fenestration systems provide energy efficiency, minimise air leakage, improve the performance of the air conditioner and cut down on the electricity consumption. The modern fenestration systems with high-efficiency glass and fixing mechanisms can cut down solar heat gain considerably. Automated intelligent systems that can align and alter themselves with respect to the position of sunlight.

What Is The Role Of Door & Window Materials In Energy Conservation?
The materials used for fenestration play a big role in energy conservation. The capability of the fenestration system to block out heat is one aspect of efficiency in terms of energy conservation. In earlier buildings of India, one would notice that thick building envelopes and small recessed openings were used to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature. But that is not desirable in the current times and in all occupancies, considering the daylight requirements.
Doors and windows contribute 30-45% of energy loss in a building. For external windows and doors, perhaps more in reference to glazed door & windows, features like high-performance glass having a right U value, solar heat gain coefficient and light transmission, are very important. Getting all the above in the right proportion is key to energy conservation. Visual Light Transmittance in the right numbers is very important for both daylight and energy.
Primary heat losses or gains from a window or door frame occur via air infiltration and thermal conduction, and to overcome this, materials such as uPVC and a good sealing mechanism can be a solution. Low-E glass is the most popular glass for energy conservation, which means a very low U value that stops the temperature from passing through the glass. Lower U values can be attained if there is the use of multiple glazing layers, gases, and low e-coating. Apart from these, other glasses with excellent solar control properties and superior protective coating play an important role in energy savings.
Explain The Performance Evaluation Of Different Door Configurations To Enhance Energy Conservation. Are There Any Tools Used For The Same? Also, Explain The Design Tools For Planning Efficient & Optimal Fenestration?
Doors can contribute significantly to air leakage, and can also waste energy through conduction, especially if they’re not properly designed, installed, and/or air sealed. There are national councils worldwide, which help to compare energy performance ratings of doors & it shows the “Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC) and U value” factor of the door is the main criterion of door ratings for energy conservation.
If exterior doors are difficult to push open because the outside air wants to rush inside, this is an indication that the building is negatively pressurised. With negative pressure, the building is likely to pull outside air in from cracks, leading to increased humidity in warm weather and chilly drafts during cold weather. A little positive pressure creates a barrier from the exterior, allowing for more control over interior conditions. The energy conservation by using windows/doors depends on the efficiency of heat resistance. Careful selection of material and technologies will help achieve the objective. As a rule of thumb, hinged doors with thermal break and deeper profiles are expected to perform well compared to pivoted and swing doors. However, the selection of doors is purely based on functional requirements.
Adding a vestibule to the swing doors or revolving doors will help in energy conservation if there is high traffic. Both casement and sliding doors offer different levels of energy enhancement. While casement doors are better for soundproofing, they are also very effective in keeping the ambience warm. On the other hand, sliding doors have thick glass and insulated frames to offer better energy efficiency.
Please Brief On Effective Glazing & Types Of Glass For Best Performance. What Is The Impact Of Types Of Glazing On Energy Conservation?

Effective glazing cuts down heat transfer and also controls temperature, humidity, sunshine and wind as per the location. Qualities like soundproof, low maintenance, fire retardant, attractive, and durability are also desired. Smart glazing for windows uses the right kind of glass with the right quality of the frame, which increases the efficiency and is a vital element because it provides light, security and helps in noise control.
There are various types of glass options for the effectiveness of glazing, like: floated glass, tinted glass, reflective glass, tempered glass and shatterproof glass. Each glass has a unique quality, and its suitability is dependent on the environmental factors as well as the requirements.
A single pane of glass provides very poor insulation because glass is a good conductor of heat. A double-glazed unit with a layer of insulated air is more efficient, whereas a triple-glazed unit with two layers of insulated air is certainly better from the energy conservation perspective. Nowadays, the innovative triple pane is also available in the market. They reflect 97 per cent of energy and only allow 3 per cent to pass through. Lastly, sandwich glass, the most efficient one, comes in various shapes and colours.
How Do You Select The Right Type Of Glazing For Your Windows?
The type of glazing is selected based on the specific project need, like the location of the fenestration, and the surrounding environment has an important role in deciding the appropriate type of glazing unit. Single glazing is the most basic form of glazing and is appropriate where visual transparency is the only criterion. Double glazing is one of the most popular forms of glazing as it has good thermal and acoustic insulation properties, and is used in building envelopes to control the quality of the interior environment. Whereas triple glazing is one of the most thermally efficient types of glazing that provides exceptional levels of thermal and acoustic insulation, but is used in special scenarios because of its high pricing.
Please Brief On The Pros And Cons Of Using Solar-Controlled Glass & Self-Cleaning Glass?
A solar control glass is a glass with a special coating designed to reduce the amount of heat entering a building. It reflects and absorbs heat as well as filters light for reduced glare.
Pros/Advantages:
- As compared to regular glass, solar control glass reduces heat gain and glare of light entering the room and provides a comfortable environment for living.
- As the heat gained in the room is less, energy conservation is more.
- They allow visible light to pass through them for daylighting.
- Tinted glasses with solar control coating are also available, which can be used to create an astonishing look for a structure.
- The exterior of the solar control glass can be made reflective, which provides privacy to the interiors.
Cons/Disadvantages:
- The major disadvantage of solar control glass is its cost. It is expensive compared to normal glass.
- In areas that experience cool climates most of the time in a year, it is not a good option, as the essential solar heat will be reduced, and there will be more need for heating the room.
Self-cleaning glass has a special coating to break down organic dirt, whilst reducing the adherence of inorganic dirt, compared to conventional glass.
Pros
- It helps in saving time and energy that goes into maintenance.
Cons
- Though it self-cleans, it does not always look very clean as expected; one would still need to clean the windows from the inside.
What Are The Key Factors To Consider While Selecting Hardware For Doors?
The key parameters to keep in mind are security, noise reduction, sealing, safety, aesthetics, durability and value for money. It depends upon the building type, function, type of door and its technical requirements as well.

What Are Your Views And Thoughts On The Future Of Fenestration Technologies?
Fenestration technology has been evolving on different tangents like aesthetics, efficiency, durability and design possibilities. And being a primary part of building façade, it has a lot of attention to it and a lot of possibilities for innovation.
A sustainable envelope through a design should be a climate-based approach. This dictates the material, building orientation and fenestration requirements of the building. In line with the climate-based design approach, the fenestration arrangement best appreciated is a window-to-wall ratio of approximately 4:6, with a vertical symmetrical orientation. In addition, a combination of basic geometric shapes can be added to give the fenestrations form and character. This is a reflection of elements such as height and shape being chosen first as being more important than aesthetic elements. Designers can leverage these elements to accentuate the fenestration and ensure that it is in line with a good understanding of the local climate of the building location. Furthermore, material specification by designers based on understanding of the immediate and current global climate change is crucial as this will determine the final comfort of occupants, reduced energy consumption and also visual sustainability of this building typology.