Cladding is one of the most expressive, inspiring and complex aspects of building design. It is the outermost skin of a building and has a multitude of roles and functions, right from providing a visual character to providing a shield against external conditions.
Various materials like metals, bamboo, timber, cellulose and hybrids have been used to construct cladding materials today. While innovation continues to happen in the facade industry in terms of material possibilities, there is a direct correlation of innovation with the evolving language of building skin designs that are driven by advanced design technologies.
Firstly, ‘cladding’ must be redefined as not just an external skin or a finish, but a surface that also goes from exteriority to inferiority of built space. So, a cladding system need not restrict to a facade or a roof structure, but rather a cladding system for an interior space. Both will have their own functions that may include, but not limited to, physical protection, aesthetics or perception.
Today, the role of a facade, interior skin or a cladding, is as complex as the building itself as it needs to strike a balance between all the parameters such as aesthetics, visual character, structural stability, solar heat gain, daylight filtration, visibility, thermal comfort, branding and programmatic zoning, among other aspects. Due to its complex nature, usually, designers opt to harness the potentials of a cladding system to either aesthetic effects or to building performance.

Very rarely, the two merge, although that’s the intent ideally. But what stops us to integrate all aspects of a cladding system in design? Is it the complexity of the problem or is it the inadequate knowledge of available design tools? Perhaps, it is a combination of both. However, both these issues can be sorted with the help of a specialist.
Emergence Of Specialists
We are currently in the age of specialization in architecture where multiple streams within the profession have emerged to create an interdisciplinary and multi-layered process of design. This has led to smarter projects as each specialist, be it energy consultants, structural designers, facade designers, project managers or architects play their respective roles to collaborate on a project. This has a direct relation with innovations in the cladding industry as well.
Looking at the importance and complexity of a facade or skin in a building, facade design specialists can take up roles of design and building of facades with their association of engineers and vendors. While there has been a lot of progress in the construction, supply and material segment of this domain, very few are focusing on the design aspect of facades.
There is also a very limited focus on material sciences and material innovation as cladding industry is currently disconnected from the designer’s need and most of the architects end up making design decisions based on what is available in the market. There needs to be a two-way process of dependency between designers’ visions and material innovations in the market for a mutually dependent innovation to occur.

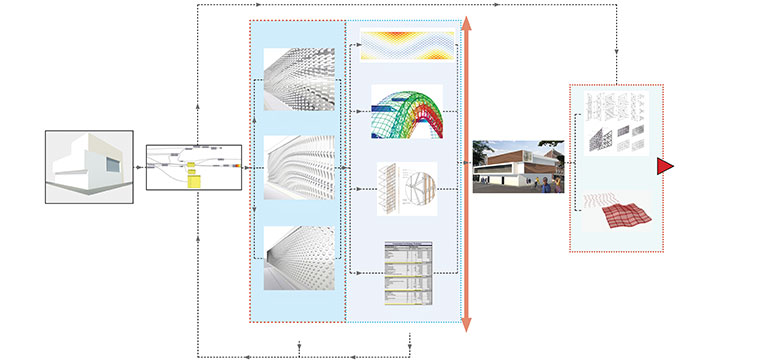
Looking at the ongoing intersections of design and technology, many designers have taken up the expertise of facade designing by use of computational design techniques, namely Parametric Design and Algorithmic Design. This allows collaborations with the architects wherein a facade design consultancy can be provided which focuses on parametric design methods that allow a wide range of design possibilities and fabrication options. This leads to explorations of cladding design possibilities at the same time wherein a designer can create a system using advanced design technologies to innovate a system for a building skin or cladding without directly relying on cladding industry’s innovation.
Parametric design, if rightly put to use, within the domain of cladding design systems, can aid in developing smarter cladding systems that can perform a multitude of tasks in an optimized way. The parametric design opens vast possibilities of controlling performance-based factors right from the early design stage of a facade project yielding results that speak beyond mere aesthetics. Since the parametric design is a technique and method of designing, we can’t truly make a fair comparison between a nonparametrically designed facade and a parametric facade, but it would not be wrong to say that possibilities of designing smarter and efficient cladding systems are made possible today with the aid of parametric methods.
Workflow For Innovative Cladding System Design
Today, designers come up with complex shapes and forms, which can be attained with a multitude of software and methods. Although the pace of change in technology is on an all-time high in this decade and we must increase the rate of innovation as we are running on a treadmill of time, methods remain the same, more or less, with new software packages allowing advancement in functionality. Parametric design is not about the software platform merely but is based on the way of designing. One can create their own customized ‘software plugins or packages’ using various coding languages, which designers are slowly getting acquainted with.

It is gaining popularity amongst designers across the globe as it can allow one to extend their creative canvases to vast avenues. Parametric workflow allows designers to take an objective and informed decisions during the process of design, where every geometry and information is associated with the building through parameters that can be controlled to produce a multitude of outputs and options. Analysis and fabrication data can also be linked in the workflow along with key parameters such as material quantities and costing.
Having an objective workflow towards design allows rational decision-making and an efficient and optimized solution for the project with respect to costs, material use, structure, etc. In a nutshell, parametric workflow harnesses the potential of computers to analyse big data and visualize complex forms and associates them to provide an integrated solution. This is an efficient use of computational design for facades and building skins.
Advantages Of An Integrated Workflow
Throwing light on one of the innovative projects from today – Morpheus Hotel (Macau) by Zaha Hadid Architects has a complex and unusual building skin that required a resolution of a cladding system to break down the complexity of geometry. Various analyses are carried out for integrated into a computationally driven workflow that leads to a resolution to find a build-able solution of the cladding system.

Another project that has an integrated parametric workflow for cladding system design is Museo Soumaya in Mexico designed by FR-EE – Fernando Romero Enterprise. This has a double curved surface form which requires a cost optimization strategy to have a cladding system that could be detailed out in a simple manner, even with the complexity of the geometry.
Having expertise in computational design, rat[LAB] Studio often delves into collaborative projects to assist in facade design and building skin development with other designers and architects by taking up the scope of parametric design consultants. Additionally, the studio also undertakes independent facade design projects by using advanced methods of designing through an algorithmic workflow. The has to lead to many explorations of cladding as we strive towards bridging the gap between available cladding systems in the market and designers’ vision.
One of the ongoing visionary projects by the studio is a collaboration with Architects Urban Zen, Hyderabad for a corporate office. The facade is quite complex as a mix of flat, single curves and double curves surfaces that define the vertical fins that blend to form horizontal members. The studio used 3D printing technology to create prototypes of the facade for creating an efficient structural and facade system and choosing the most appropriate cladding system.
Another collaborative project by rat [LAB] with Urban Zen, Hyderabad, a fluid facade language is explored on a 20-storey building in Hyderabad using parametric and computational methods which requires a cladding system that has to be light-weight yet visually solid loaded on a conventional structural system. Innovation happens in such projects by following a non-linear integrated workflow to achieve a complex result.
In another recent facade project by the studio, the skin of the building is envisaged as a porous surface with punctures made through CNC cutting of MS Sheets, while globally emerging into a continuous pattern when seen from a distance. Interpreting from the brand identity of the client, a pattern is generated para metrically, with variable punctures emerging out from a central focal point, spread on the full facade of 3300 Sq ft as a pattern that cuts direct glare, brings in indirect illumination into the space, as well as marks the building with a highlight feature on the busy street affront. The pattern is fragmented into 40 panels of regular sizes placed on an MS Grid Framework, anchored to the building slabs. Each panel is numbered for quick sorting and site assembly which come together to form a patterned facade for a banquet cum boutique hotel space.
Since cladding systems are not only restricted to exterior building skins, interior spaces provide their own set of opportunities and possibilities. In an interior design project of an Experience Center by rat[LAB] INTERIORS, a faceted language is spread to create a shell-like cladding system that integrates high-tech design tools with low-tech construction strategies.

Four surfaces (three walls and a ceiling) are mathematically subdivided into triangles of varied sizes and angles through computational methods that allow optimization of material and construction time. CNC (Computer Numerically Controlled) milling is carried out on large slabs of Marble Stone to generate 3-dimensional surfaces clad on to surfaces at different angles. Each marble stone, as an individual triangle, is further subdivided to form smaller fractals leading to ridges and valleys.
Similarly, in another project by rat [LAB] INTERIORS, residential space is transformed by adding an innovative cladding system, but this time with a fluidic wavelike artistic gesture. Space was developed with the intent of having fluidity in space as a wave captured in motion.
This project demonstrates the use of mathematically driven algorithms that transform the orthogonal nature of contemporary furniture or art into fluid forms and curvilinear morphology. These algorithms have been used to generate formal sculptures that are then constructed from digitally formed timber profiles and painted with a weather-resistant polyurethane coating, among other finishing alternatives.
In a recently finished restaurant project by rat [LAB] INTERIORS, a faceted cladding system is designed as an articulated and expressive language that physically and visually connects the ‘outside’ and ‘inside’ leading to a vibrant cohesive space.This exhibits a true blend of cladding innovation for interior and exterior space.
For innovation to occur in the cladding industry, there needs to an integrated workflow where design, fabrication, materiality and structure can all be considered in a seamless workflow. This can happen with an appropriate blend of technology and design for architects to achieve efficient and smarter results.














