No matter where it originates, from railways, aircraft or factories, noise is all around. Future trend research suggests that traffic and noise in general will only get worse. The careful and considered selection of glass can be crucial in helping to reduce noise level and meet noise requirements. In a fast urbanizing society, sound is one of the most significant causes of stress and fatigue. The irony here is that sound is a silent killer and most people do not know its significance. Many new buildings are using glass extensively, and many without any consideration to how well a glass façade will block sound.
Sound
Sound is a vibration that propagates as a typically audible mechanical wave of pressure and displacement, through a medium such as air or water. In physiology and psychology, sound is the reception of such waves and their perception by the brain.
The two factors which determines the loudness and pitch of sound is Intensity (db) and Frequency(Hz)
Intensity:
The amount of energy that is transported past a given area of the medium per unit of time is known as the intensity of the sound wave. The greater the amplitude of vibrations of the particles of the medium, the greater the rate at which energy is transported through it, and the more intense that the sound wave is.
![]()
Typical units for expressing the intensity of a sound wave are Watts/meter2.
Mass Law:

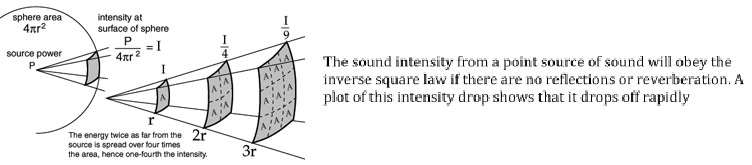
Inverse Square Law:
The Threshold Of Hearing and The Decibel Scale:
Humans are equipped with very sensitive ears capable of detecting sound waves of extremely low intensity. The faintest sound that the typical human ear can detect has an intensity of 1*10-12 W/m. This faintest sound that a human ear can detect is known as the threshold of hearing (TOH).
Frequency:
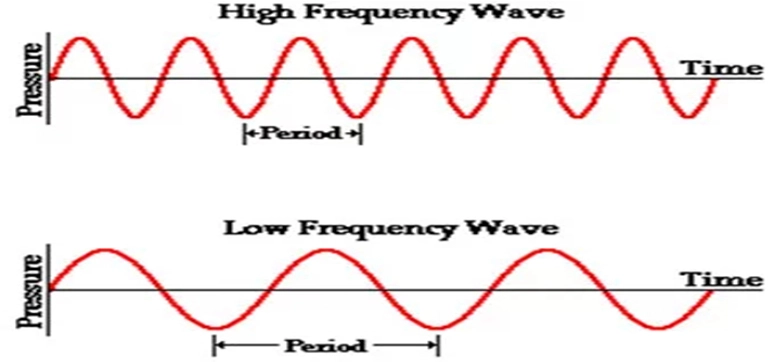
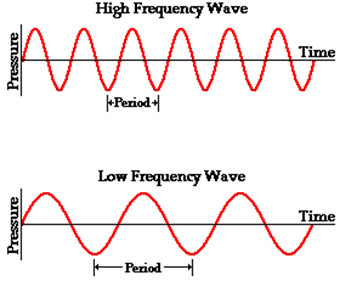
The vibrating object which is creating the sound wave, the particle of the medium through which the sound moves is vibrating in a back and forth motion at a given frequency. The frequency of a wave refers to how often the particles of the medium vibrate when a wave passes through the medium. The frequency of a wave is measured as the number of complete back-and-forth vibrations of a particle of the medium per unit of time. If a particle of air undergoes 1000 longitudinal vibrations in 2 seconds, then the frequency of the wave would be 500 vibrations per second. A commonly used unit for frequency is the Hertz (abbreviated Hz), where
1 Hertz = 1 vibration/second
The diagram below shows two pressure-time plots, one corresponding to a high frequency and the other to a low frequency..
Frequency, Pitch and Human Perception:
The ears of a human (and other animals) are sensitive detectors capable of detecting the fluctuations in air pressure that impinge upon the eardrum. The human ear is capable of detecting sound waves with a wide range of frequencies, ranging between approximately 20 Hz to 20 000 Hz. Any sound with a frequency below the audible range of hearing (i.e., less than 20 Hz) is known as an infrasound and any sound with a frequency above the audible range of hearing (i.e., more than 20 000 Hz) is known as an ultrasound. The sensation of a frequency is commonly referred to as the pitch of a sound. A high pitch sound corresponds to a high frequency sound wave and a low pitch sound corresponds to a low frequency sound wave.
The ability of humans to perceive pitch is associated with the frequency of the sound wave that impinges upon the ear. Because sound waves traveling through air are longitudinal waves that produce high- and low-pressure disturbances of the particles of the air at a given frequency, the ear has an ability to detect such frequencies and associate them with the pitch of the sound. But pitch is not the only property of a sound wave detectable by the human ear.
Acoustics in Glass Facades:
In a fast urbanizing society, sound is one of the most significant causes of stress and fatigue. The irony here is that sound is a silent killer and most people do not know its significance. Many new buildings are using glass extensively, and many without any consideration to how well a glass façade will block sound.
How to Improve Acoustic Insulation Through Glass?
Glass of each thickness will have the same level of acoustic insulation. It is primarily through the ability to combine different glasses that acoustic insulation properties of facades can be improved.
- Usage of thicker glass: The simplest and most effective way to protect against sound is to use thicker glass.
- Asymmetrical Double Glazing: Due to resonance it is better to use glasses of different thicknesses inside the insulated glass units. These will resonate at different frequencies thereby giving slightly better sound protection.
- Increasing the air gap between IG units: Increasing the air gap between the insulated glass units has a very significant impact on sound reduction. The spring – weight – spring effect will be attenuated by the additional air.
- Using laminated glass: Laminated glass is made by laminating two pieces of glass with a poly-vinyl-butryl (PVB) interlayer. The interlayer dampens the sound and reduces sound transmission. Lamination also provides other benefits like safety and security. Laminated glass improves sound insulation due to dampening effect of PVB interlayer.
- Using different configuration of glass, noise can be reduced by up to 55 to 60 dB.
Factors which do not affect sound insulation:-
- Tint/color of glass
- Coating (Reflective or Low-E) on glass
- Position of glass
- Tempering
SOUND REDUCTION (DB) IN DIFFERENT CONFIGURATIONS OF GLASS :
Conclusion:
In the urban environment, sound is one of the most significant pollutant. While using glass extensively in building facades, one need to consider how well a glass façade will block sound. Glass of each thickness will have the same level of acoustic insulation. Hence thickness of the glass to be used for a building faced should be decided based the noise pollution level in the surrounding. Acoustic insulation properties of facades can be improved by combining different types of glasses. Higher air gaps between the insulated glass units have a very significant impact on sound reduction. Usage of laminated glass also reduces the pollution level.