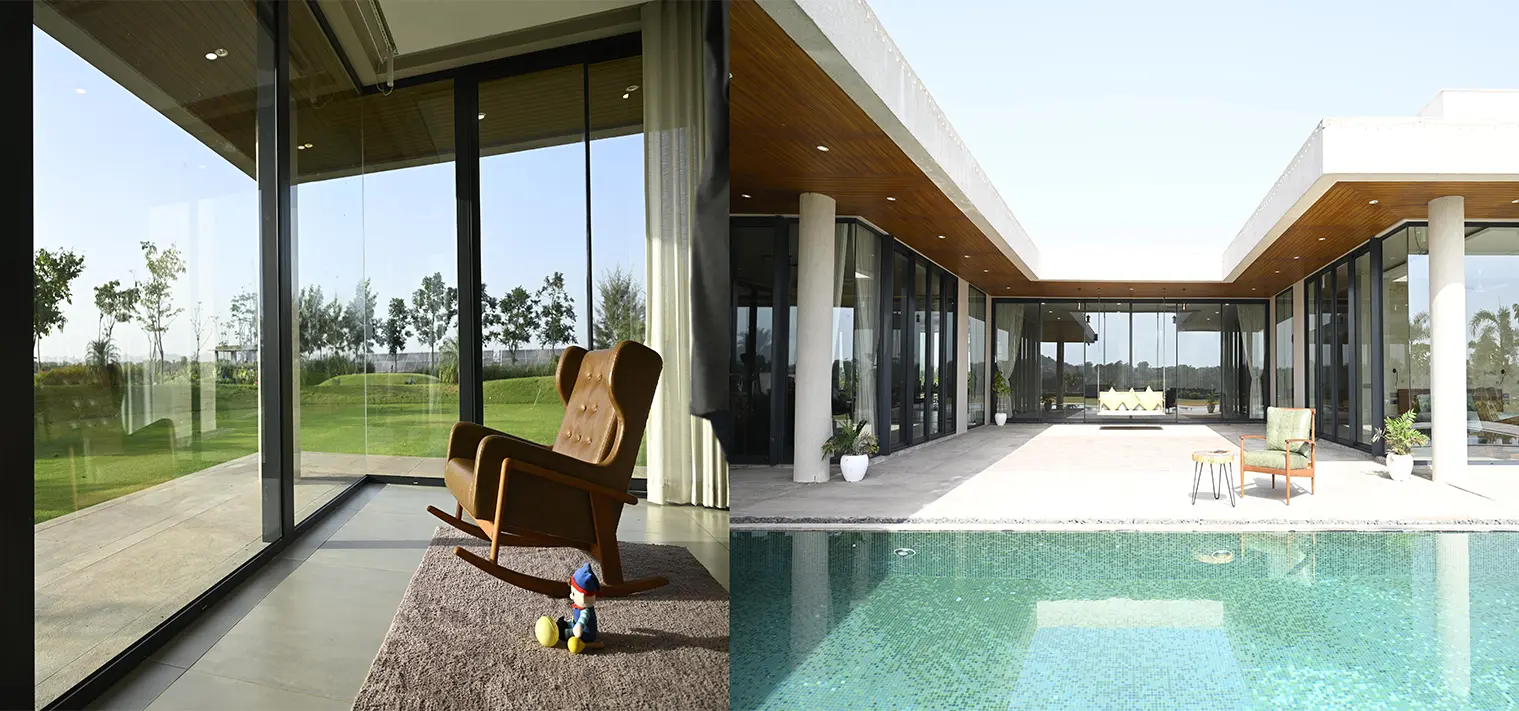
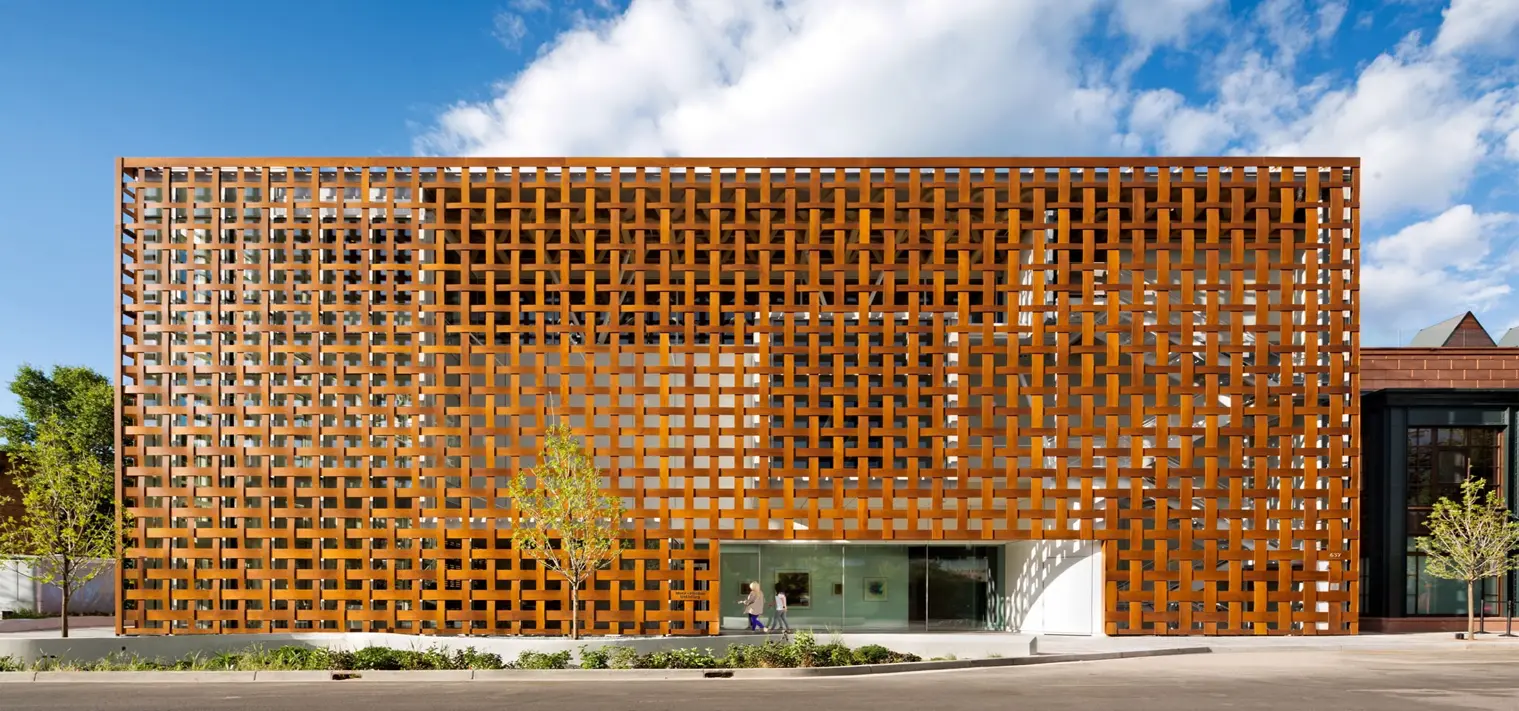
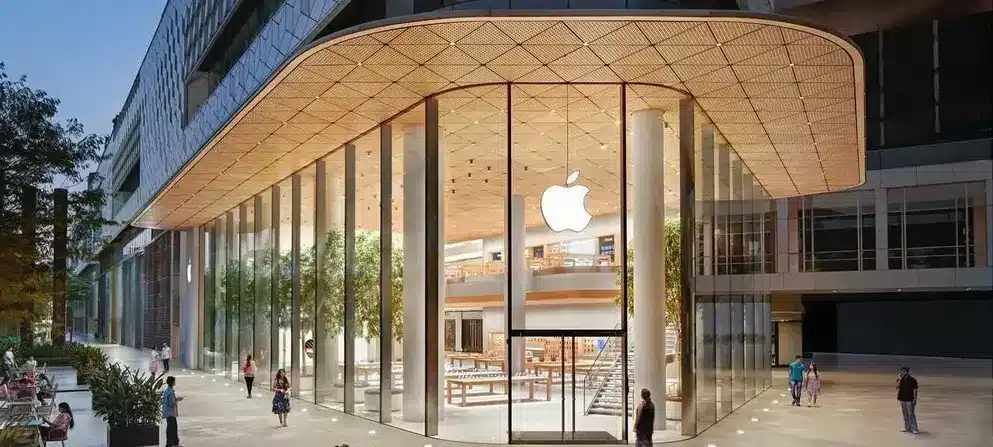
The main challenge being faced today by the building material industry is the appropriate selection of products for building façades – Glass being one of the main products.
With the available options here are a few pointers that will definitely help in the specifications of getting the desired inputs:

1. Orientation: Building orientation plays a tremendous role in energy performance & occupant productivity. Solar heat gain and daylighting can vary greatly depending on the path of the sun in the summer versus the winter. South-facing façades must allow for solar heat gain control, while north-facing façades require less solar protection. Overlooking these can result in excessive heat gain or glare issues that could compromise energy performance and occupant comfort.
2. Colour and Transparency: The colour and transparency of glass can significantly impact the aesthetic appeal of a building’s façade. Clear, coloured, or frosted glass can create unique and interesting visual effects, while transparent glass allows for maximum visibility and light penetration.
3. Texture and Pattern: Textured and patterned glasses can create an artistic and dramatic façade while providing privacy to the interior. Various glass types such as acid etched glass, sandblasted glass, laminated glass, and fritted glass must be chosen depending upon their effect on the façade.
4. Lighting: The use of glass walls and façades can create a beautiful lighting effect both inside and outside the building. Interior lighting and dynamic façade lighting can enhance the design element and aesthetics of the building.
5. Reflectivity: Reflective glass can create a modern and sleek appearance in buildings, reflecting the surrounding architecture and landscape. Care must be taken to ensure that the reflective properties of the glass do not create glare for neighbouring properties.

6. Framing and Structure: The type of framing and structure used for the glass façade can significantly impact visual aesthetics. Slim frames or frames with hidden fixings can create a contemporary and seamless appearance.

7. Strength and Safety: The glass must be able to withstand the forces that it will be subjected to, including wind pressure, snow load, and impact resistance. Specially engineered glass types such as Toughened Glass, Laminated Glass, Insulated Glass, etc., must be chosen based on the requirement.
8. Thickness: The thickness of the glass must be chosen based on the building’s location and the size of the glass pane. For example, stronger winds in a particular location may require thicker glass to be used to prevent breakage.

9. Climate Control and Energy Efficiency: The type of glass used must be selected to provide climate control and energy efficiency in the building, considering the local climate and orientation of the building.
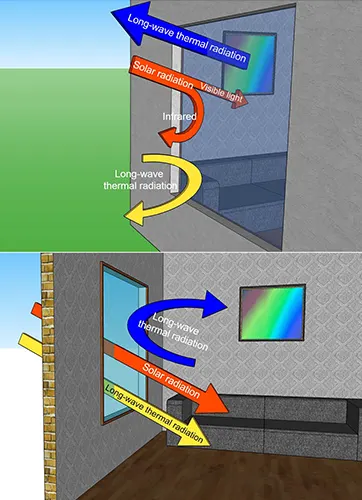
10. Acoustic Insulation: Glass must provide adequate acoustic insulation to reduce the amount of noise entering the building.
11. Ultraviolet Rays: Among the biggest advantages of the right selection of glass is its ability to provide solar control and glare control. This is particularly advantageous as it controls harmful UV rays and therefore glass goes a long way in ensuring occupant comfort, health and safety.
12. Maintenance: The glass must be designed to be easy to maintain and clean. It’s crucial to consider the water-repellent coatings that would prevent water from seeping and streaking.
13. Cost: The cost of using glass in buildings is also an essential consideration. Depending on the type of glass required, the cost can vary significantly.
14. Building Codes & Standards: Glass must be installed in compliance with local building codes and regulations.
Overall, selecting the right type of glass for construction requires considering factors like aesthetics, energy efficiency, strength, safety, climate, and acoustic qualities. It is crucial to work with qualified professionals who have experience in specifying glass for building construction














