Building envelope and along with it facade engineering is evolving with creative designs and new building materials to cope with aspirational designers and educated building owners. More emphasis is being given to the humble facade with rising awareness amongst the building owners and developers in order to create value which was long lost and to extend the life of the buildings and finishes. However during the process of these creations one witnesses a number of experiences where failures and poor performances are evident which upsets the designers and the owners/creators. This article aims to share a few real time experiences of failures covering several facets of the issue.
Etiology of Façade Failures

Generally failures are attributed to several aspects and it is highly unlikely that a single factor would result in facade failure. Facade elements are combinations of several materials combined together in a specific build-able form that is integrated as the building envelope. During the complete process from design to implementation, there are various steps that are involved. Each process has to be handled with utmost care and precision by specific teams adept in the respective skill.
Hence, the failure etiology is quite complex. In many situations findings from the failure investigations are highly challenging and it’s difficult to conclude the primary cause.
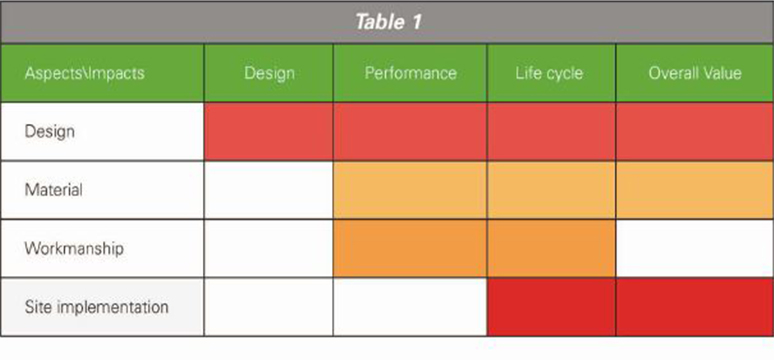
Table 1 presented here illustrates critical aspects of the process which help in identifying the failure analogy. It also represents the level of risks associated with the aspects and its impact on the finished building facades.
Types of Façade Failures
Following is the explanation of some of the major aspects varying from design, materials, structural and integration that culminate into facade failure.
Aspects of failures

Possible Causes: Panels stacked one above another | No vertical movement allowance
~ Structural
~ Pertaining to material
~ Incorrect design and detailing
~ Implementation
~ Integration
~ Underestimating complexity
~ Ignoring building behavior
~ Poor Integration with buildings
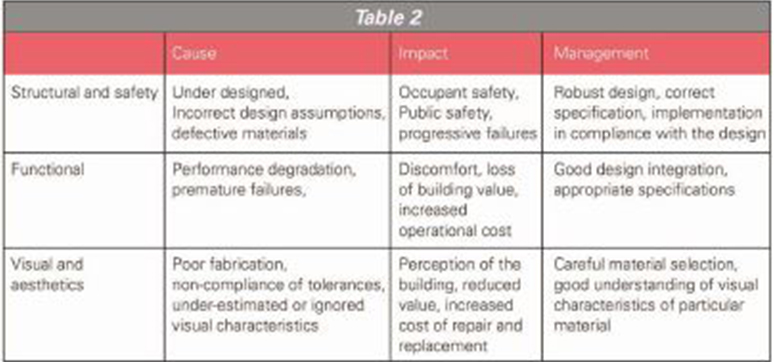
Structural Failures

Generally result from the following major reasons:

Possible causes: Incorrect material specification, i.e., combustible materials used | Cladding panels are not fire resistant | No vertical separations
• Incorrect design
• Underestimating building behavior
• Complex and impractical designs
• Poor implementations
These failures will have serious impact on the facades and may pose safety issues in front of the occupants.
Material Failures
These failures often cause major disruption in building services and life safety. Major factors resulting in material failures are listed below:
~ Incorrect materials
~ Ignored long term performance
~ Unknown life cycle
~ Not suitable for a particular weather
~ Premature due to local conditions
Material and finish generally undergo premature degradation resulting in alteration of life cycle and incur significant replacement cost. Failures are generally attributed to the aspects such as compatibility, weather exposure, etc.

Glass Failures

Glass failures generally result from the following key aspects. Following images shows some classic failure patterns.
Nature of Failures & Non-compliance of Glass
~ Structural
~ poor processing
~ In appropriate specification
~ Poor performances
~ Inherent material characteristics
Images 8-12 show some classic glass failure patterns
Managing Glass

Glass is often complex and requires good experience with specialist skills in order to meet the expectations. Visual non-conformities are generally considered as non-compliance rather than failures. Following are tabled out some key aspects to note.
Implementation Failures
Failures during the implementation are primarily combined effect of several teams not working in tandem. Few key aspects are presented below:
Inappropriate design:
~ Design not suitable to site condition
~ Poorly designed details
~ Incorrect dimensions

Incorrect site sequences:
~ Poorly planned work flow
~ Mixed sequences of different trades
Site modifications:
~ Prefabricated parts modified at site to suit site conditions
~ Tolerances are out of control
Poor coordination and site management
~ Miscommunications between the teams
~ III prepared for the site conditions
~ Unclear responsibilities among team
Missing quality management
~ Dedicated quality-checks are missing
~ Systematic checking procedures not in place.
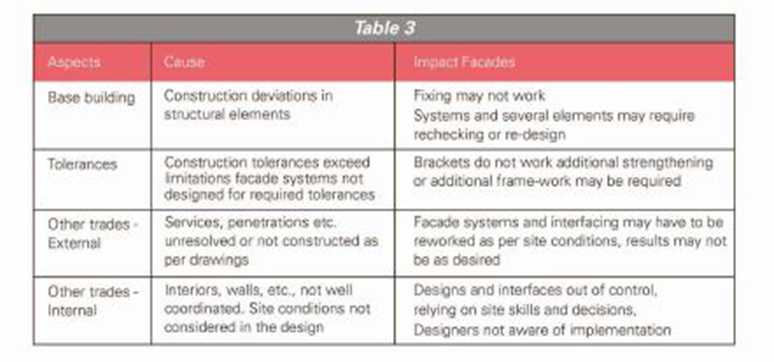
Integration/Interfacing Failures
Inadequacies during the interfacing stage and integration with the main building have a major impact on resultant functionality resulting in failures ultimately. Few key aspects are tabled.
Conclusion
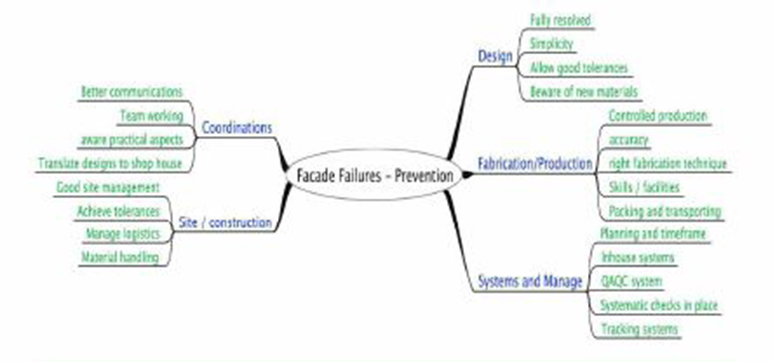
Failures generally surface as a result of a combination of several factors, right from design to implementation. Often the tracking of failure is not an easy and pleasant task as it deals with finding faults at several stages and a lot of stake-holders are involved. Hence it is essential that adequate level of management systems is in place to avoid potential risks of building façade failures.














