A novel design or use of material in one instance, becomes commonplace after repeated use over time. The basic morphologies, materials and processes that comprise the technology are well-tested and of known performance validated from use. Concurrently, a proliferation of highly visible structural glass façades in the built environment has resulted in the dissipation of perceived risk among the building community and the public and an increasing acceptance of the innovative technology. As a result, interest in utilizing structural glass façade technology is increasing among architects and their owner-developer clients. The next tier of adopters is primed. Structural glass façade technology is poised for significant potential growth, but barriers remain.

The demands on building systems have increased in many respects over the past several decades. Nowhere are these demands greater than with the building skin. Architects are demanding more design control and more diverse aesthetic possibilities out of the available cladding options. At the same time, as energy costs rise and rapid climate change emerges as a looming threat, developers, architects, and increasingly, government and regulatory agencies are mandating improved thermal performance in building façades. Of course, as long as the industry keeps on limiting itself to the common systems which in fact are limited. Yet, there are solutions that indeed are better in terms of safety, sustainability and cost-effectiveness. A few of these shall be covered in this topic.
Fenestration: Door & Window Systems
In designs for façades of residential buildings in city centres, conflicts of interest often arise. On the one hand, the residents want an adjoining outdoor space, and, with the prospect of greater demand and higher prices per square meter, it is in the investors’ interest to fulfil this desire. On the other hand, the cantilevers and cut-outs accompanying balconies and loggias disrupt the homogeneous appearance of the façade and the urban character of the city. In particular, most recently, with the increased popularity of residential high-rises, the question has arisen of how to make generously dimensioned outdoor spaces available to the residents that can also be used when there are strong winds, inclement weather, or low temperatures.
A) Turn & Tilt Windows
The turn-and-tilt-lift window contributes to the perception of spaciousness because all of the profiles are hidden from view. The major advantage is that the openings are restricted to two angles and are not unidirectional. If the desired opening angle is less, then the tilt function of the window can be used and by turning the handle this state of tilting can be changed to a fully opened window.
B) Lift & Slide Doors

The lift & slide door system offers three significant advantages over conventional sliding doors. The doors run on two multi-wheel carriages engineered to provide maximum support and incredibly smooth movement. Superior sealing capabilities engage when the door is in the locked position. Dual weather seals at the top, bottom and sides actually become tighter with increased door size. Lift & slide doors are sill-supported and designed to resist air and water infiltration better than other sliding door options. Multiple operable door panels slide and overlap each other, opening up amazingly wide spaces. Operable sliding panels combined with fixed panels result in a remarkable number of size and configuration possibilities, including corner units with no post.
C) Parallel Opening Windows
The leaf or louver is moved outwards and downwards in an Arc. As a result, the advantages of a circulating and safe ventilation function are combined with an increased ventilation cross-section in the projecting element. The new system is based on solid stainless steel opening levers, which replace the stay technology that was used up to now. This system enables the air free flow, regulating the temperature.
D) Sliding & Folding Doors
This system was developed to enable almost any object to slide or fold. The gear systems are available as straight sliding or folding systems or be used in stacking doors/windows, pocket doors/windows or multiple-grouped folding doors/ windows. The system can also be used for wardrobes, cabinets, cupboards, interior doors and room dividers (partitions). The residential gear application is considered to be any installation involving individual door weights of up to 100 kg. Door weights higher than 100 kg are required to use industrial gear. Doors/windows are to be supported with on-bottom rollers depending upon the building structure and permissible loadings.
Façade: The Cable Supported System

Structurally, a cable is a non-rigid member that takes only tension and has no rigidity. A cable sagging under its own weight takes a catenary shape. When uniformly loaded, it is usually assumed to take on a parabolic shape. From these basic assumptions, equations can be derived that relate the sag, tension and change in length. One curious aspect of the analysis is that it is analogous to an arch in pure compression and the basic equations are essentially the same. Loads suspended in tension provide an alternate paradigm for building. Instead of stacking a structure until it reaches its apex, as most buildings are constructed, cables allow a structure to be hung from a mast or armature. Other aspects of the design that should be considered are corrosion protection and in-service inspection, effects on the structure due to removal and replacement of cables during the lifetime of the structure, vibrations and dynamic loading, fire resistance and fittings. Some examples of the fittings include swaged and socketed fittings, clamps and, in the case of some cable net glass façades, custom steel castings have been used with great success.
- The classic project done at Munich Airport in 1993 known as the Kempinski Hotel (now Hilton), uses the world’s first cable net. The elegant-looking façade is as tall as 20 meters in height and around 22 meters in width.
- The Shanghai Diamond building is yet another landmark cable net system with a height if around 60 meters, 1 single cable per panel from top to bottom supports the whole façade. The glass clamps and cable net made the 2400 sq mt area possible to stand on. The vertical cables are 36 dia and the horizontal ones 16 dia.

The Cable Supported System-Kempinski Hotel
Why Cable Systems?
Think about the intent to have a sleek yet transparent façade, indeed point fixed support systems have been fitting the frames. Driving such intent of luxurious, transparent and elegant looks is the supporting structure, and none the least is the budget, but to what extent and what system? And most importantly, one needs to consider sustainability in the long run. Such cases have led to a lot of projects being held for a long time, intent changes, and internal collisions in the industry; As a result, the urge for evolving the technology is no longer largely comprised of experimental structures. It has been tried and tested in a considerable diversity of built forms; structural systems have been adapted to façade applications; specifications and methods have been developed, tested and disseminated; practitioners have built hundreds of highly innovative façade structures in a variety of applications; development costs have been absorbed. An infrastructure of material suppliers, fabricators and erectors has developed in response to

increasing project opportunities. Of the supporting system, the industry tends to follow the general trends. Commonly used are the MS pipe/beam and glass fin supporting structures, certainly with limitations.
For Example, to construct a façade using a point fixing system with a height of more than 12 meters
- In the case of MS pipe/beam as the span of the façade increases vertically, the diameter of the pipe increases and so does the thickness thereby shooting the costs sky high.
- In the case of glass fin, the width and thickness of the glass increase at the same time. So where is the transparency and sleekness of the structure?
Are We Limited to Use Stainless Steel Cables Only?
Well, the answer is no, there are options such as the galvanized iron cables, whose costs are as low as 50 per cent of what an SS cable can cost. These cables are called the Galfan cables with a special coating called as the epoxy zinc-rich prime.
Introduction on Zinc – 5% Aluminium-Mixed Rare Earth Elements Coating
With the gradual worsening of air pollution, the corrosion of wires and cables become more and more serious. The results show that most of the corrosion on wires and cables in nature happens due to the electrochemical process, so the study and search for new anti-corrosion coating is an effective measure to prevent and inhibit the steel products from electrochemical corrosion. The current anti-corrosion technology has been developed greatly and anti-corrosion work has been developed in a wide variety of coating structures, even has its own characteristics.
The Zn-5%Al-AE alloy coating is the most extensively represented as Galfan common worldwide. This kind of coating developed in the early 80s of last century is a new type of hot-dip coating used to coat steel wire or other steel products. This alloy has been developing rapidly in the application of coating steel since its advent, from steel plate, steel strip, and steel pipe to steel wire.
Galfan is a kind of eutectic alloy combined with 95 per cent zinc, 5 per cent aluminium and trace rare earth alloy elements. The patent of this kind of new-style technology belongs to the International Lead and Zinc Research Organization(ILZRO). The mass fraction of eutectic-Al is 5.2 per cent, and the melting point is 382°C which is even 37.5°C lower than that of pure zinc(419.5°C).
- It has high corrosion resistance, which is 2-3 times higher than ordinary galvanized. Whatever severe environment, in the lab, outdoors, in wet conditions and in marine climate, the corrosion resistance of Zn-5%Al-Mixed rare earth alloy coating is superior to ordinary hot-dip galvanized and electro-galvanized.
- The ductility and variability of Zn-5%Al-Mixed rare earth alloy coating is extremely strong, even exceeding its protective steel base. Compared with ordinary coating, it does not produce the brittle Fe-Zn alloy interlayer, but the Fe-AL-Zn alloy formed at the cross interface of Zn-5%Al- Mixed rare earth alloy coating and the steel base. The Fe-Al- Zn alloy has very good ductility and adsorption with a steel base is strong, so it can stand strong under the conditions of the winding deformation process, and bending test, without having to worry about cracking and shedding. 3) The Zn-Al structure in Zn- 5%Al-Mixed rare earth alloy coating provides excellent surface uniformity. Compared with other coatings, the alloy coating itself is an excellent pre-adhesive substrate and daub adhesive, which can be applied to improve cracking corrosion and blistering after the daub. What’s more, this kind of coating steel wire, steel strand and wire rope can be further coated.
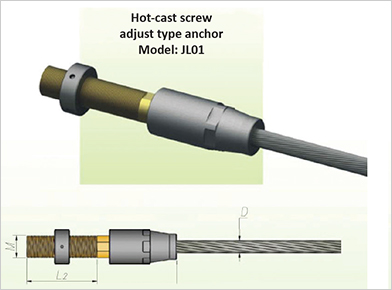
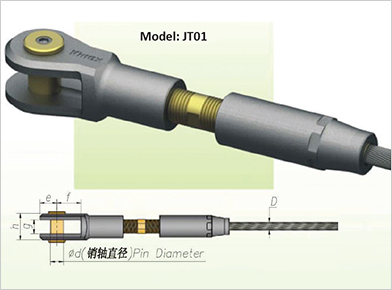
| Chemical Composition of Cable Swaged-End (Galfan Cable) | ||||||||
| Chemical Elements content (%) | ||||||||
| C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Ni | Mo | Cu |
| ≤0.50 | ≤0.60 | ≤0.90 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.35 | ≤0.40 | ≤0.20 | ≤0.40 |
Surface Finish for Cable Swaged-End: Epoxy Zinc Rich Prime
Epoxy zinc-rich prime corrosion resistance system is recommended, reasons as follows:
- Epoxy zinc-rich prime is very easy to match with finishing paint, has good adhesion, and excellent physical mechanical properties, has good glue strength to finish paint at the same time, easy desiccation under normal temperature, and not colours bleeding to finishing paint.
- Partial coating scratches and impacts usually occur, when steel tension rods are transported or installed, it need partial touch-up.
- Steel structure needs spray coating when it is constructed before acceptance inspection. Steel tension rods can spray coat together with them, keeping the construction style the same. It can avoid wasting production costs because of repeating spray coating.
Post Railings: LED Integrated Railing Solutions
To complement the balustrading handrails, there is finally a method of incorporating the latest in LED technology in a slimline, unobtrusive method that adds style, beauty and elegance to your home. LED-based handrail, that delivers functional illumination. Two intensities may be specified: standard output and high output. The standard light output version delivers luminance levels appropriate for exterior applications as well as for dark interior environments with low ambient illumination levels (e.g., themed environments, theatres and residential areas). The high output version delivers luminance levels applicable to interior environments – providing in excess of along the path of egress.
- A weatherproof High CRI LED light strip with waterproof adhesive for easy installation
- Innovative Feeney light diffusing lens
- Connection and installation accessories
- 24 Volt DC Constant Voltage 35w, 60w, or 96w:(Optional AC power cable available)
- 24 Volt DC Constant Voltage Dimmable Driver 40w, 60w, or 96w
- This remote-controlled dimmer system is designed to work easily with LED kits to help create the perfect level of lighting.

Conclusion
In conclusion to the article, as the market is growing by the day, the construction materials sector has a lot of potential in the coming years. At this point, do we understand the importance of the process of choosing the hardware? Are we enlightening ourselves to understand the recent market trends? The hardware we consider is small in size and few in quantity but very important and powerful in functions. Without the hardware, the system can’t withstand and function well. Time for us to look and investigate more details, and dig out the best with proper comparisons for fruitful and deserved results.














