What are the common causes of building fires?
Building fires occur due to misuse of spaces for functions and uses not intended or planned and designed. National Building Code of India prescribes the requirements of life safety, fire prevention and fire protection, and are well-detailed each of 9 occupancies.
Causes of fire:
- A building planned and designed for specific occupancy is used for alternate occupancy and the fire load risk increases.
- Misuse and malfunctioning and overloading of MEP Services such as air conditioning systems, short circuit in electrical installations
Please throw some light on various façade/fenestration materials reaction to fire.

National Building Code of India specifies the fire resistance rating of the materials to be used in façade in Part 4 and new section 8 in Part 6, and also the active fire protection system for the glass assembly (glass and framing) used in building façade. It is imperative to have the façade and fenestration materials to meet the specifications and fire resistance rating as required by National Building Code of India, to ensure leap-frog fire spread aspects are mitigated and assembly protected.
What are the parameters which define the performance of a fire retardant façade/fenestrations?
Non combustibility is an important aspect to align on fire retardant /resistant façade/ fenestrations. The integrity of the system from structural and fire safety considerations is imperative. It is to be ensured that the overall assembly meets this requirement. There are aspects of surface flame spread which also plays an important role in the selection of the materials. While the internal active fire protection system helps and aids to control the fire within the inside of the event zone, however the fire rating of the façade and fenestration helps to control the spread of the fire and issues relating to leap-frog fire spread.
What are the aspects to consider and precautions to be taken while designing and installing fireproof or fire-resistant facades and fenestrations?

As mentioned above, designing and installing fireproof or fire-resistant facades and fenestrations requires materials and also assemblies have the non-combustibility features and to meet the requirement on control of surface spread of fire in the façade. It is also imperative to have passive fire sealant between slab edge and façade elements to prevent the spread of fire with-in the building along the internal side of the façade. This includes compliance to firestop materials to control/eliminate the spread of fire.
Tell us about fire-resistant materials that can be used on facades/ fenestrations.
Materials are available to demonstrate the fire resistance, non-combustibility, surface flame spread, drip test which are required to be selected aligned to NBC. In other countries, aspects as above are varied based on height of building. But in India, the requirements were consistent inconsequential of the height.
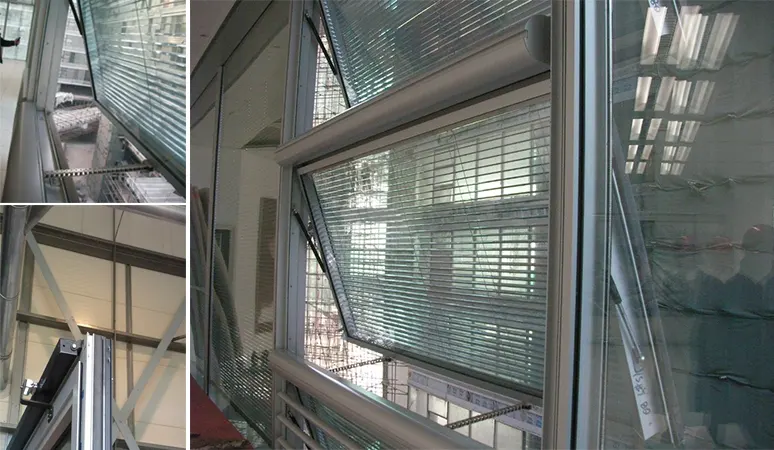
How can glass be a fire-resistant material? How does an interlayered toughened fire glass work?

There are various manufacturing processes through which fire resistance glass can be achieved. Detailed process of manufacturing fire resistant glass to meet the specific requirement of integrity for the defined duration of fire resistance could be obtained from OEMs where global manufacturing standards and processes are followed.
Explain active and passive systems for fireproof facades/fenestrations. How can we prevent fire spreads?
Active system comprising of provisions of sprinkler for façade glass protection is included in Part 4 of NBC 2016. It is noted that a well-designed and functional fire protection system (sprinklers) would be able to aid in control of fire in the inside of the building. However, based on some experiments conducted towards enhanced coverage of sprinkler from the inside of the building on the façade glass, helps in timely cooling of the glass and maintain the integrity of the glass.
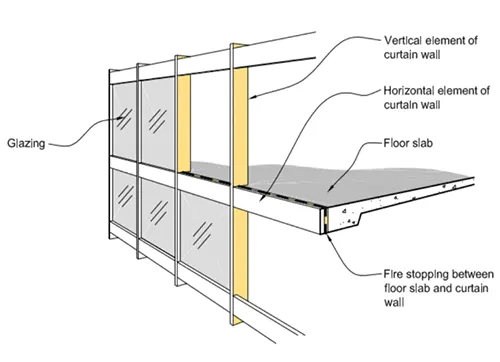
Passive system comprises of fire-stop to be provided at the slab edge and the façade elements. The same is also included in NBC Part 4, 2016. These two aspects are integrated in active and passive approach in the control of the fire spread. Further smoke heat exhaust ventilation systems (SHEVs) with 10% openable (NBC of India provides for it) can also have actuators which can open glass manually or automated linked to fire detection and alarm systems with Tested Solution Range. EN 12101 provides additional norms. Façade consultants and glazing fabricators and system suppliers have to work together for thal mel (integrity).
What are fire barriers and fire-stopping systems?
Fire Barriers and Fire Stops are passive fire control systems and are planned to maintain the fire compartmentation of the areas inside the building. It is imperative to have fire compartment planned in building to prevent the spread of fire which also helps in damage control of assets and importantly helps in evacuation of the building occupants.
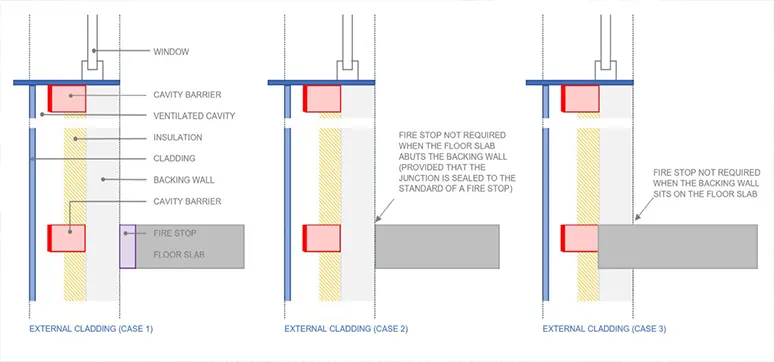
The fire barriers and fire stop are to be selected for specific areas and to maintain the integrity of the compartment area. These are to be duly labelled and to be inspected for its purpose as installed. Any breaching of the fire barrier and fire stop are to be controlled and corrected.
What is the need for Fire rating requirements on the façade/doors/ windows and the exterior wall systems?
The insistence of non-combustibility, fire flame spread and fire resistance criteria of façade/doors/windows and the exterior wall systems is to avoid issues of spread of fire externally on the façade of the building and to ensure life safety of occupants from fire and smoke spread. In certain situations, where the refuge areas are outside with façade areas and glass being between refuge and inside areas of the building, the code specifies to have 2-hour integrity of such elements to be with fire barrier to avoid exposure of fire to the people in refuge areas.















