Could you please explain some of the common causes for fires in Buildings in the Middle East? How can fire risks be reduced?
Fires are mostly caused by human error and fire usually starts small before it becomes large and uncontrollable if the proper action is not taken or if the fire spread mitigations are not in place. The fire spread mitigations are fire detection and alarm, fire extinguishing and fire control, and passive fire safety. All these need to be maintained and malfunction of one of those systems can cause fires to develop.
Please explain the role of design in fire-safe buildings?
A design that incorporates fire safety measures will lead to reduced risks of fires spreading and developing but it also allows people to escape safely in case of fire and allows firefighters to access the buildings effectively.
What is the role of fenestration design in fire-safe buildings?
Most building design aspects have a fire safety component so does fenestration design. Fenestration design can have an influence on the vertical fire compartmentation, fire spread, and in some cases the fire escape. The façade designers are now liaising more and more with the fire engineers to make sure that their design meets the safety standards.
What are the passive & active fire-safe protection methods?
Fireproofing of materials; making sure that separations (walls, doors, other openings) are made in such a way that fire and smoke cannot pass for a certain time period and making sure that building materials do not contribute to the fire spread all fall under the umbrella of passive fire protection. Active fire protection measures that require a certain action which can be for instance make a sound when smoke or heat is detected or release of fire extinguishing products in case fire is detected.
Reaction and fire resistance: How are materials classified in the event of a fire?
Materials are classified according to their flame spread rating and smoke development. There are products that hardly or don’t spread flame or produce smoke and there are products that produce burn rapidly and produce a lot of smoke. Products are classified as classes A, B, or C (or Class I, II, and III) according to different institutes such as ASTM or BS or EN. Apart from the products, there are also tests required for a complete wall or façade assembly.
The flame spread rating should not be confused with the fire-resistance rating of walls and structures. The fire-resistance rating is usually expressed in hours and defines how long a product can resist a fire under a certain standard fire test.
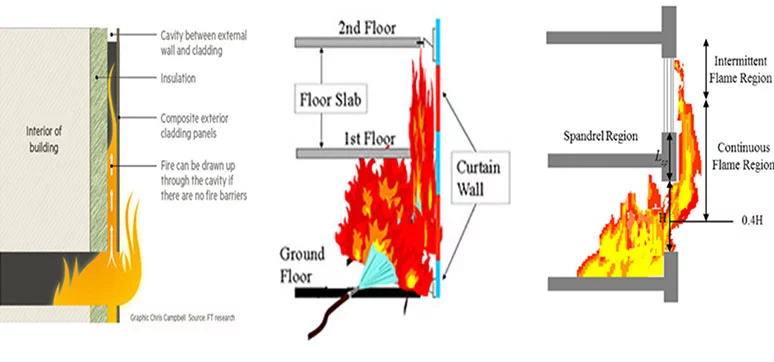
What scenarios could cause an internal building fire to spread to the external façade and other parts of the building? What protection measures are in place to control fire?
There are two possibilities for an internal fire to spread to the façade to other parts of a building. The first one is the leapfrog effect where the fire spreads from one opening to another opening in the wall. For the purpose of a fire spread, an opening can also be a glass window as glass might burst when exposed to fire. The second one is the chimney effect the fire spreads between the floor slab and the façade wall or simply through the cavity between the external wall and the cladding.
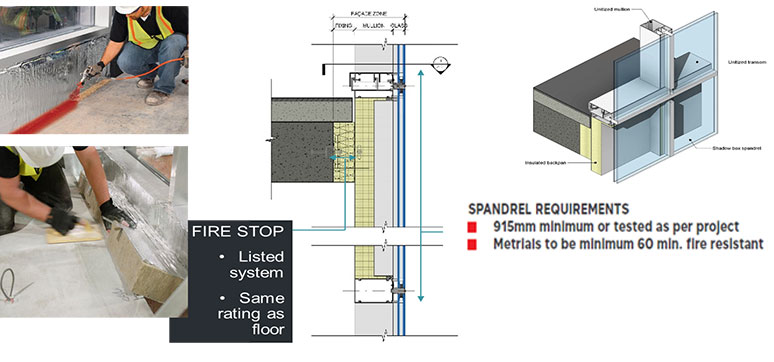
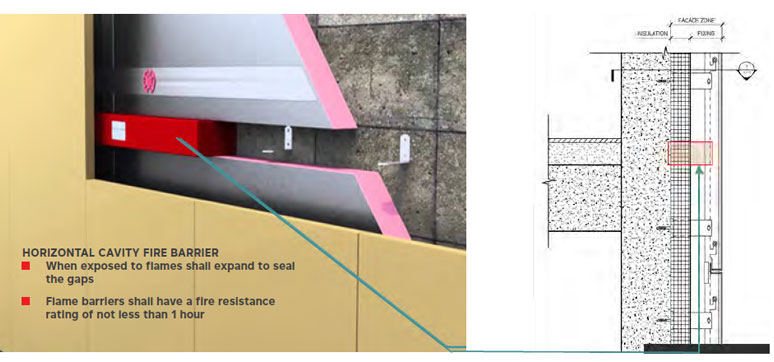
The protection measures in place are the previously mentioned product specification related to flame spread and required fire ratings of floor slabs, especially when it comes to the connection between the floor slab and the façade. Also putting fire breaks or fire barriers in the cavities between the external façade and cladding are techniques that are applied to prevent the spread of fire.
What is the importance of ‘perimeter fire barrier systems in the prevention of fire spread?
The perimeter fire barrier system refers to the prevention of fire spreading through the gap between the façade and the floor slab. The fire barrier element or system should be of the same fire resistance as the floor slab and should be fitted properly in the space between the floor slab and the façade element. The perimeter fire barrier system should prevent fire from spreading from one floor to another through the floor slab.
Brief about the choice of materials considering fire safety.
As mentioned before, materials must meet the requirements regarding flame and smoke spread. These requirements are specific to the occupancy of the building and to the height of the building. More stringent material requirements apply for a high-rise hotel or a hospital as compared to a low-rise factory.
What do you think about the current fire safety codes for buildings in the region?
The current fire safety codes in the various jurisdictions in the Middle East have become well developed regarding façade fire safety in the last couple of years. The main reasons are that there are a lot of high-rise buildings or buildings with special façade features that are constructed and still being constructed and, unfortunately, several façade fires happened in recent years.
As a result of a number of façade fires, the UAE fire code has been overhauled in its 2018 edition. There is also an ever-increasing awareness not only with the various civil defense authorities but also amongst the building owners, property developers, contractors, and designers when it comes to fire safety. People start to understand that building that is not fire-safe have significantly less value.