Fire safety in airports is a major issue. What are the main causes for the same relating to the façade and fenestration design?
Since airports are extremely important public buildings and mass transit areas, occupied by thousands of people at any point, fire and life safety are very critical. Combustible exterior cladding materials present an increase in fire hazards which result in fire incidents. Most death incidents are related to smoke exposure and toxicity rather than direct flame and heat exposure. Falling, burning debris can be a significant hazard and can cause downward fire spread. Hence the use of fire-safe façade cladding materials, which are absolutely non-combustible and fall under Class A1 /components with the limited release of toxic smoke (A2-s1,d0) by the third-party accredited certified testing laboratories, is critical to ensure complete safety of human life and property damage. Airport design should not compromise on the material specification with respect to the fire code. Guwahati airport has carefully scrutinized each exterior material specification and ensured a thorough study on the active and passive fire protection.
What is the role of façade and cladding materials and installation technologies on the fire safety of the airport?
The new international Terminal Guwahati Airport Building featuring façade and roof focuses on high-performance building facades designed in order to provide optimum light transmission, solar control properties, thermal insulation, control annual heat gain inside the building, which in turn will provide a reduction in HVAC tonnage and can result in energy savings. There are six entry vestibules provided for the arrival and departure area, comprising of pre-coated aluminum perforated sheets with a dented pattern for a three-dimensional effect, and solid panels cladding the entrance portal frame.

In order to achieve an efficient building envelope, the external envelope of the terminal building and fixed link bridge has been designed with a semi-unitized high-performance glass curtain wall. The opaque façades of the airport feature Zinc-Titanium alloy interlocking panel cladding, GFRC cladding, extruded terracotta cladding, and fiber cement board cladding, in relation to its reaction to fire behavior, meets the requirements to be classified as Class A1 (Non-Combustibility Rating) as per EN 13501-1 /DIN 4102- 1 /Class 0 as per BS 476-Part 6 (Fire Propagation Index) & BS 476-Part 7 (Surface Spread of flame).
The roofing system of Guwahati Airport comprises of insulated Zincalume/Galvalume standing seam roof. The roofing system is installed with mineral wool (stone wool or glass wool) materials as part of a system that contributes to achieving fire performance requirements, better tolerances to withstand high temperatures without losing its properties and integrity, translate to longer effective lifespans as well as provide better insulation against heat. These factors add value beyond the fire resistance performance of the building element.
Multicell Polycarbonate roof skylights are integrated into the pitched metal roof due to their lightweight,100% leak-proof, excellent thermal insulation properties which result in energy efficiency and cost savings. Translucent Co-extruded UV-protected Multicell Polycarbonate panels are designed to be flame retardant and are tested against fire as per EN 13501-1 in an internationally accredited laboratory and classified B-s1, d0.

Please throw some light on aspects such as façade openings, ventilators, and other façade designs that would help to prevent fire and its spread?
In case of fire, for smoke extraction of the double-height area at the departure level, louvers are provided in the facia and behind the same, smoke exhaust fans are proposed on the city side and airside façades. For these smoke fans, since it is not advisable to puncture the façade components, isolated supports are provided for the exhaust fans. A separate system like roof truss is provided for supporting of exhaust fans.
What is the importance of ‘perimeter fire barrier systems’ in the prevention of fire spread?
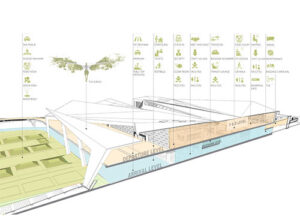
Compartmentation of airport terminals is vital in slowing the movement of smoke and containing the fire until help arrives. Challenges faced during fire emergencies are smoke spread (toxic gases), it caused breathing issues, suffocation and impaired vision, hard to access areas for firemen due to thick smoke and fire preventing them from fighting the fires. Poor compartmentation or non-fire-rated materials lead to the LeapFrog effect due to the external spread of fire. So, façade compartmentation in passive fire protection acts to contain fires to a specified area of a building or structure. Fire stop and smoke seal perimeter fire barrier system (Fire resistance-minimum 2 hrs fire rated) play a pivotal role in preventing fire and smoke propagation from one floor to another.
What is the role played by building plans & layouts helping reaction to fire stairways & escape routes, signage, use of fire retardant glass in the interiors, etc.?
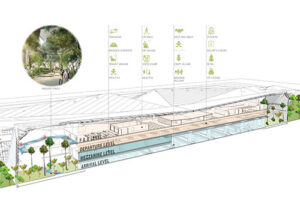
Fire protection techniques are an indefinite combination of variables such as the typology of the project, height of the building, planning strategies, user experience and activities pursued by occupants, fire behavior characteristics of different materials, to name a few. The objective of planning a building should suffice measures that provide the highest degree of safety from the fire and an integrated approach that minimizes danger to life and property.
A fire evacuation and prevention system is more than identifying exits; perhaps it refers to prescribing both the minimum and maximum standards of fire protection with logic and comprehension. In a nutshell, the process entails demarcation of fire zones and fire exists supported with appropriate signage, adopting building construction practices that adhere to fire resistance norms, and adapting to innovation and technology-based fire evacuation systems.
Please discuss the guidelines, standards, and norms for fire-safe façade materials and installation by the Government/ other authorities/ NBC. Are there any design specifications too? (including the norms and standards by the UK and the USA, which are followed in India)

In India, European (EN) / German (DIN) / British (BS) International standard codes are followed for Fire Protection / Safety. Out of these, EN 13501- 1 (Fire classification of products) are mostly followed since it is the most stringent standards in which materials are classified in Euro classes – A1, A2, B, C, D, E &F which are tested for combustibility (temperature where combustion starts) & Ignitibility (Point from where the product will ignite).
All the materials classified A2, B, C,& D in EN norms obtain an additional classification regarding the smoke emission LVL & the production of flaming droplets and/or particles (Flaming droplets of cladding materials needs to be tested which leads to secondary fires due to falling debris). The flame spread index is checked separately in EN Norms. Additionally, Reaction to fire Testing should also include an assessment of fume toxicity.
Please discuss the special policies/ specifications by the Government/ NBC for buildings with glass/ACP/ HPL claddings, preventing fire spread.
National Building Code (NBC) 2016 Part 4-Fire & Safety incorporates the necessary fire prevention provisions for life safety and protection of buildings.
Putting some limelight on the latest technologies/equipment for firefighting

Actuators for Automatic Smoke Vent – Actuators are electronic drivers that open and close vents for the purpose of smoke and heat exhaust ventilation. Actuators are connected to control modules. During an emergency scenario, the actuation of the actuator can be from the BMS signal input provided at control modules or a switch.
Breakable Glass with Red Triangle Marking – Fully tempered & heat soak single or DGU glass can be provided which can be breakable with the help of a hammer in case of a fire emergency.
Fire Fighting Drone Technology – Infrared drones can be used by firefighters. Drones, when equipped with a thermal camera, allow an incident command to see through smoke to direct firefighters where the hot spots are and also have the ability to see through the smoke and low light conditions.

Drones allow firefighters to quickly and effectively scout out dangerous fires, observe and monitor a large blaze and the surrounding area, and more.
Drenching to cool the glass during the fire – Drench firefighting additive is a liquid additive, which is poured into the water supply and is designed to dramatically reduce extinguishing time when fighting fires. Drench can be used safely and quickly to extinguish any combustible material.
Kirti Arora did B.Arch (Hons) from Mumbai University and has over 15 years of work experience in the field of architecture and the façade Industry. Having gained significant understanding & experience in façade material properties, technical specifications & detailing, she is currently involved in around 6 airport projects as a façade consultant.














