With rapid urbanization in developing countries, need to reduce environmental impact and building energy costs have never been greater. Indian construction industry is at a critical juncture wherein it has to balance the demand of low cost construction but simultaneously comply with the stringent environmental & efficiency norms that are becoming order of the day.
Building services engineers now have the capability to challenge existing concepts for energy reduction and investigate alternate materials and façade configurations that affect building’s electro-mechanical designs and have a direct consequential impact on the project’s capital and operating costs.
With majority of buildings in India expected to be constructed in next three decades, the experts are working towards creating a balance between the technology from western world and old wisdom of Indian buildings that evolved over a period of time in harmony with nature.
Building Façades
Façades as a building envelope form the outer skins of buildings as a project image and creative intent. The façade is also the focal point of the Energy efficiency in a building design because it works as the first frontier to face the intense heat and a major source of heat ingress into the buildings. As an enclosing building component, it connects or separates the interior and the exterior. All components of the building façade, therefore need to work together to regulate the indoor environment, responding to heating, cooling, ventilation, and natural lighting needs. It must balance requirements for ventilation and daylight while providing thermal protection appropriate to the local climatic conditions.
The optimally designed building façade is an important factor not only for achieving the energy efficiency, but also the human comfort for which the buildings are actually designed. A thoughtfully designed skin can make a new building work more effectively for its owners, occupants and environment. It can also transform the performance of an existing building.

Trends & Implications of Façade Designs
Traditionally we had buildings with thick walls, small windows, huge attics and cross-ventilation. The trend has gradually emerged in recent decade, driven largely by the pursuit of transparency in the building facade. Use of glazed building façades in modern buildings gained popularity because of enhanced views, building’s reputation and attracting International companies. However, if not designed consciously, these design approaches have significant impact on capital cost of electrical and mechanical systems and building’s subsequent operational cost.
In addition to economic aspects, building façades have both positive and negative effects on work performance as well. Negative effects are associated with discomforts, distractions or health risks that interfere with peoples’ ability to do their work whereas positive impacts are associated with enhancing work performance, psychosocial well-being, and health to enhance the overall performance.
Facade Implications on Occupant Health& Performance
Performance enhancement is more likely to come from a different set of building features and attributes that affect performance. Lighting that produces glare or visual discomfort is more likely to be associated with headaches and eye problems. Glare due to direct solar penetration and due to the lack of luminous uniformity across the space distorts the perception of good indoor day lighting.
As per a field study of office workers, it is found that workers who had window views of nature felt less frustrated and more patient, and reported more overall life satisfaction and better health than workers who did not have visual access to the outdoors or whose view consisted of built elements only. The positive effects of nature may also extend to the immune system, thereby directly affecting human physical health.
Thereby, one of the perennial challenges in designing facades is to achieve an even distribution of diffused daylight across the building section.
Use of Computer Simulations for Façade Optimization
In order to achieve optimized façade design from energy efficiency, Cost efficiency and occupant comfort perspective, there are specialized computer simulations conducted viz. Wind CFD Analysis, Solar &Daylight Analysis, Glare & Visual Comfort Analysis, Natural Ventilation Analysis etc.
These computer simulations conducted at different stages of the projects help optimize the building designs to enhance performance and achieve comfort at the same time. The simulations are aimed to evaluate building designs for identifying potential concerns and providing solutions to ensure appropriate façade design by identifying the most feasible and cost effective options for the project. The quantified results help owners, architects and engineers to take informed design decisions.
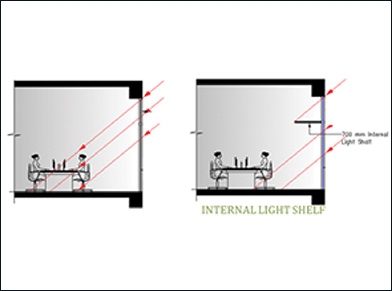
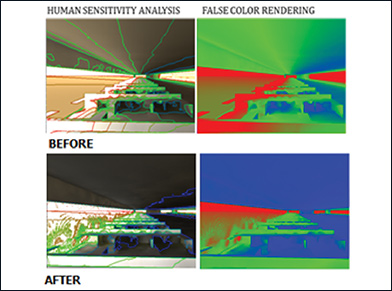
Fig.1 and 2 are the images that demonstrate the pattern of direct sun ingress into space and subsequent placement of workstation to achieve glare free daylight in indoor spaces:
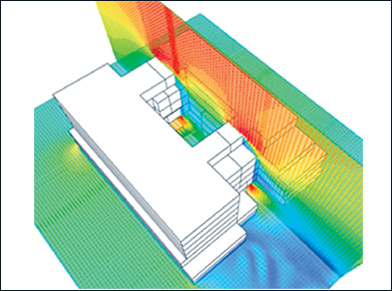
Fig.3 is the image of Wind CFD analysis conducted to optimize the window openings within the courtyard of this office building.
Facades of Future
Catering to the demands of an ever expanding industry and innovative designers, the future technologies in building façades will provide better efficiency, aesthetics and commercial value to the developments addressing a wider spectrum of issues covering following:
• Facades Generating Power Photo Voltaic Glass Unit (PGU)
Building integrated photovoltaic’s capture the solar radiations and turn it into energy. A high level of energy generation (up to 12 per cent efficiency) can be generated through Photovoltaic Glass unit. The advantage of this technology is that it is allowing the usage of fenestration part of the building as PGU’s provides transparency to human eye up to 70 per cent.
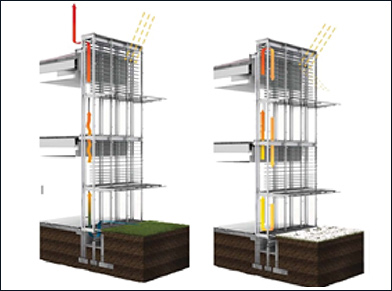
• Living Facades
A living facade is a vertical surface incorporating vegetation into its structure or face to facilitate various aesthetic, environmental, social or economic functions and benefits. While research and studies on the subject are limited, it is thought that living facades could make a significant contribution to sustainability if properly integrated.
Also known as; living walls, vertical greenery systems, vertical gardens and vertical vegetated complex walls, they should not be confused with green walls (the process of allowing climbing plants such as ivy to scale a wall while being rooted in the ground).
A wall mounted, modular three dimensional, green façade system with plants showing seasonal interest
• Interactive Facades
The interactive façade will have to include systems that correct or moderate the performance of the glass as the outdoor conditions change, also allowing for individual occupant adjustment of the indoor comfort parameters. In last few years, technological advancements have gone a step ahead as a result of which technologies like phase change materials, motorized external shades, automatically controlled integrated blinds in DGUs, motorized internal blinds are already available. This is a positive indication in this direction and buildings are certainly accepting the same depending on the respective business needs and project budgets.
• Dual Skin Facades
The dual skin façade can be simply defined as a system that consists of an external screen, a ventilated cavity and an internal screen. Solar shading is positioned in the ventilated cavity. The external and internal screens can be single glass or double glazed units, the depth of the cavity and the type of ventilation depend on environmental conditions, the desired envelope performance and the overall design of the building including environmental systems.


• Facades Enhancing Indoor Environment – Growing Fresh Air
Most developing countries have high pollution levels and as a result the indoor environment can be even more polluted. Drawing ventilation air through a green façade or a greenhouse offers a potential to counter the toxins, VOC’s, microbial infections etc. in an air-conditioned building.
• Facades Addressing Food Crises – Hydroponics
The idea that fruits and vegetables can grow with water, light and nutrients are the basis of hydroponic: one of the innovative systems of making the building self-sustaining. There have been other numerous advantages of this system as well. A reduction is seen in street level concentrations up to 40 per cent for NO2 and 60 per cent for particulate matter. They potentially contribute to an increase in biodiversity in urban areas by providing a habitat for birds etc. The most important aspect is their “Rejuvenating effect” on the living creatures around as they contribute in softening of the urban landscape and allowing buildings to seem more ‘natural’ and pleasing to the people.


Conclusion
Energy efficiency is a primary challenge in today’s commercial construction industry. How important are energy efficiency gains from a building envelope is a topic that is gaining momentum amongst industry-leading architects and design firms. In order to address a few paramount issues in the industry, with ever-increasing pressure for the dual objectives of higher performance and improved payback calculation to stakeholders, innovative trends and forces shaping the future of building skin contains the answer of many unfolded domains.