In the present day, there is a worldwide concern about high-rise buildings’ façade fire risk. Building façade provides the barrier between the internal and external environment in terms of stopping of water and air infiltration, and by thermal and acoustic insulation. Besides, building façades play another role in terms of the appearance of the building. Conventional masonry walls and facade materials were capable of providing the required barrier and insulation but did not allow the flexibility and lightweight needed for high-rise buildings and the most attractive and innovative buildings’ forms and elevations that the new façade systems provide.
Some of the modern façade systems include facade materials like metal panels – Metal Composite Materials (MCM), Aluminum Composite Material (ACM) system, glazing, etc. – which are used for the outer surface of the exterior wall/façade. Another set of facade materials / items are also being used to enhance the energy efficiency of the building like thermal insulations, which are fixed between the outer/external façade layer and the masonry wall.
 The Address Downtown Hotel Fire, Dubai
The Address Downtown Hotel Fire, Dubai
Thermal insulations are necessary for places where heating or cooling is essential to maintain the internal comfort temperature higher or lower than the external ambient temperature, and for a longer period of the year. Along with the aesthetic and sustainability appeal, these modern façade systems invited fire safety concerns also. In the last two decades, several major exterior wall fires have occurred in high-rise buildings and façade systems utilizing foam plastic based insulation materials are found to be responsible for the severity of the fire spread.
Research works have been initiated long back, however, the fire risk related to façade systems has attracted more serious attention after the Grenfell tower fire in London, which took 71 lives. Multinational forums had been organised to gather information about façade fire incidents and materials responsible for that from all over the world.
Some of the Major Fires are:
• The Wooshin Golden Suites in Busan, South Korea, on October 1, 2010 — ignition attributed to a spark from an electrical outlet
• Polat Tower, Istanbul, Turkey, on July 17, 2012 — ignition attributed to a faulty air conditioning unit
• Mermoz Tower Roubaix, France, on May 14, 2012
• Tamweel Tower, Dubai, on November 18, 2012 — ignition attributed to a cigarette discarded onto a pile of waste materials
• Saif Belhasa Building, Tecom, Dubai, on October 6, 2012
• The 40-story Grozny-City Towers Chechnya, Russia, on April 3, 2013 – ignition attributed to a short circuit in an air conditioner
• Al Tayer Tower, Sharjah, UAE on April 28, 2012 — ignition attributed to a cigarette
• The 63-story Address Downtown Dubai hotel on New Year’s Eve 2015— ignition attributed to an electrical short circuit
• Baku, Azerbaijan, on May 19, 2015, with 16 people killed and 63 injured
• Two residential towers in the city of Ajman on March 28,2016
• The 1,105-foot (336.8 meters) Torch Tower in Dubai — which Initially burned February 21, 2015 — and whose exterior façade burned a second time on August 3, 2017
• Water Club Tower at the Borgata Casino Hotel, Atlantic City, New Jersey, on September 23, 2007
• Grenfell Tower in North Kingston, West London, on June 14, 2017
(Source: fireprotectionengineeringdigital. com and others)
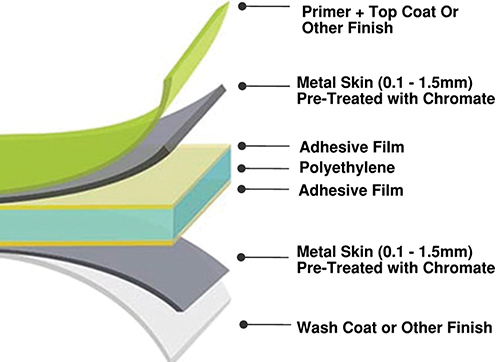
The study of the collected information revealed that for most of the cases, Metal Composite Materials (MCMs) systems, especially the insulation materials are responsible for the severity and fast growth of the fire. A typical configuration of MCMs is shown in the graphics, for ACMs the metal is aluminium. Note the core material inside the two aluminum surfaces is polyethylene.
A thin sheet (about 0.5mm) of metal (especially a soft metal like aluminium) are not resistant to fire, rather metals are combustible when in dust or thin sheet form. It is a known fact that metal dusts are used in pyrotechnic, which means if the surface area is more compared to the mass of the metal and its temperature is raised to a certain temperature at which the metal burn or is oxidised in air. That temperature, at which a metal burns varies from metal to metal and for metal like aluminum it is much less than a flame temperature of common combustible or flammable items.
In a typical configuration of a modern exterior wall, as seen in the graphics, thermal insulations are fixed to the masonry wall surface. A gap is maintained between the insulation and the outer surface. This gap, if not sealed at regular intervals, works as a free space for air and flame to travel and spread.
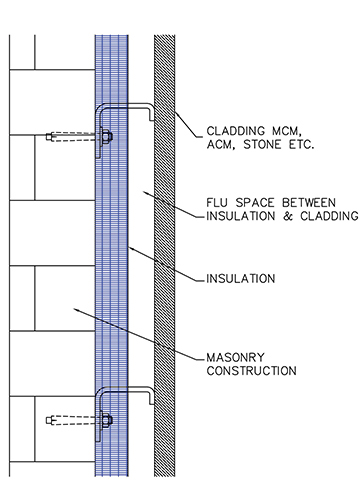
Foam plastics have been used as thermal and acoustic insulators in the external walls and have contributed largely to façade fires. In addition, foam plasticbased insulations used in these systems can contribute to fast growth and spread of fire on the external wall surfaces. The study of fire incidences revealed the foam plastic attributed to façade fire was not in compliance with any established guidelines.
The assemblies are generally called External Thermal Insulation Composite System (ETICS – in Europe) or Exterior Insulation and Finish System (EFIS – in North America). Testing of the façade system assemblies is necessary for some standardised testing schemes to assess their contribution to fire development and spread when used in buildings. Several external walls’ fire tests were developed and are widely used globally, including NFPA 259, 268 & 285 and ASTM E84.
Façade systems testing and subsequent installation/ application in buildings must include all materials and components assembled in the exact tested configuration to ensure a reasonably safe system application and limited acceptable fire hazard.
Some countries have already banned the use of these foam plastic-type insulations. As an alternative, Rockwool insulations are being used. Rockwool is a non-combustible material but scores less as thermal and acoustic insulating material compared to foam polyurethane (plastic) which is used as insulation. There are some other advantages of foam polyurethane, it is lighter than Rockwool and its stiffness is higher, which makes it easier to install, it is also better in waterproofing. These advantages have resulted in the wide use of foam polyurethane as insulating material.
Grenfell Fire Study
In 2006, the tower was refurbished with an insulated rain screen façade system consisting of combustible polyisocyanurate (PIR) foam insulation and aluminum polyethylene composite material, separated by a ventilated cavity covering the exterior of the building. On 14th June 2017, a fire started in a fourth-floor apartment, broke out to ignite the recently installed façade system, after which it spread very rapidly around the outside of the building, and into almost all the other apartments. The individual different components of the façade system were certified by tests for fire safety, although it is not sure whether the refurbished façade system was actually compliant as an assembly.
It should be noted that in 2006, restrictions on use of combustible facade materials on the exterior walls of high-rise buildings were relaxed in the UK, where targets for energy efficiency were prioritised.

Test Methods – Questions have raised whether the test parameters for facade materials are sufficient? Because the selection of building materials is done based on the test certificates, especially for high rise buildings where materials are usually carefully selected and would never be used without having appropriate performance test certificates. So, when an installation fails, a question on test certification of the material is valid.
Many experts put their opinion stating that the small-scale test scenarios do not reveal many fire behaviors of facade materials that come into effect in a real-life full-scale scenario. One of the reasons for such fire incidents is that small scale tests could not identify the risk hidden in the facade materials which would appear when a large quantity of the same material is exposed to fire.
The installation plays a great role in the performance of any system. An inaccurate installation can jeopardize a whole system. For example, use of foam plastic, combustible insulation, was allowed considering that this will be covered properly that an external fire cannot reach the insulation material. A poor quality inappropriate installation can expose these insulation materials to external environment and hence an open flame.
Violations – Being a 3rd party fire consultant, we come across several material datasheets, test certificates, application procedures, etc. on regular basis. Test certificates of some materials and their assemblies specify the installation criteria and limitations, and the materials are usually certified based on the assumptions that they will be installed in accordance with the procedures stipulated in the test certificate. However, in reality, the same is not observed. Insufficient quality control procedure leaves loopholes in the protection system.
New developments in ACM have been introduced by some manufacturers. Mineral wool is being used between the aluminum surfaces instead of polyethylene. This would reduce the severity of fire risk. The test report from a renowned laboratory shows the ACM has a self-ignition temperature of 530oC and a flash ignition 520oC when tested per ASTM D1929-16. However, the certificate categorises the ACM as Class-A per ASTM E84-16, having the Flame Spread Index (FSI) 10 and Smoke Development Index (SDI) 15. The certificate also classifies the material as A2-s1, d0 per EN13501-1:2007+A1:2010.
Test results of the different methods state the material is noncombustible (A2-s1, d0 category per EN-13501), the material has a flame spread and smoke development property and also the material can ignite spontaneously at elevated temperature. So, it becomes the responsibility of the designer to ensure the test parameters are in line with project parameters.
ASTM E84 test results are generally used for the selection of interior finishes. The interior of the building can be protected by a sprinkler system. A limited flame spread and smoke development along with cooling effect of sprinkler provide a tenable environment for the occupants to evacuate the building. Also, the possibility of the flame to spread to other areas vertically or horizontally is limited.
Arguments in support of using the above-mentioned material as placed by the owner and designer can be summarised as:
• The material is class-A per ASTM E84
• The building is sprinkler protected
• The material is used on the outer surface, so the occupant can evacuate the building safely
• The external walls are not required to be fire-rated by fire codes; and so forth.
These arguments have not come for the first time, probably combustible materials had been allowed in external wall construction based on these arguments.
Responses to these arguments are also put forward by some experts, in short those can be stated as:

• Sprinkler system does not have any effect on the external surface of the building, a fire inside a sprinkler protected building can still break through a window and ignite combustible material in external wall.
• Fire from one floor travels to upper floors through windows and involve the apartment in a fire, and then the upper floor of the newly involved apartment. These scenarios are observed in many incidences even when the external wall is masonry and does not contribute to fire growth. Now the effect can be imagined when the external cladding material is combustible and can contribute to fire growth, of course the situation will be worse.
• Sprinkler systems are generally designed for simultaneous operation of 12-15 sprinkler, in case the external cladding contributes to fire growth and involve several floors, this may activate several sprinkler heads much more than it is designed for, resulting in insufficient or no water discharge at higher floors.
• Generally, high-rise buildings are designed for phased evacuation, considering the limited vertical fire spread due to fire-rated floor construction and vertical shafts. But since the façade fire travels vertically, this will trigger the need for evacuation of all floors together, resulting in overloading in the stairs and possibility of stampede.
The conclusion of this discussion can be drawn as mere code compliance is not sufficient, as new materials are being introduced in the industry at a faster pace than the test methods and standards are being upgraded. The latest information about the selected material along with fire investigation and study reports must be referred prior to selecting facade materials and systems . A comparison between the test parameters and the application scenarios must be made prior to selecting the system or material for any particular project. It should be noted that all those buildings that were involved in façade fires had used certified materials only.